How to Set Up PostgreSQL Apache Iceberg Replication
Ever wanted to run high-performance analytics on your PostgreSQL data without overloading your production database or breaking your budget? PostgreSQL to Apache Iceberg replication is quickly becoming the go-to solution for modern data teams looking to build scalable, cost-effective analytics pipelines.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about setting up real-time CDC replication from PostgreSQL to Iceberg, including best practices, common pitfalls, and a detailed step-by-step implementation using OLake. Whether you're building a modern data lakehouse architecture or optimizing your existing analytics workflows, this tutorial covers all the essential components.
Key Takeaways
- Protect Production Performance: Offload heavy analytical queries to Iceberg tables, keeping your PostgreSQL database responsive for application traffic
- Real-time Logical Replication: PostgreSQL WAL-based CDC streams changes to Iceberg with sub-second latency for up-to-date analytics
- 50-75% Cost Reduction: Organizations report dramatic savings by moving analytics from expensive PostgreSQL RDS to cost-effective S3 + Iceberg architecture
- Open Format Flexibility: Store data once and query with any engine (Trino, Spark, DuckDB, Athena) - switch tools without data migration
- Enterprise-Ready Reliability: OLake handles schema evolution, CDC recovery, and state management automatically for production deployments
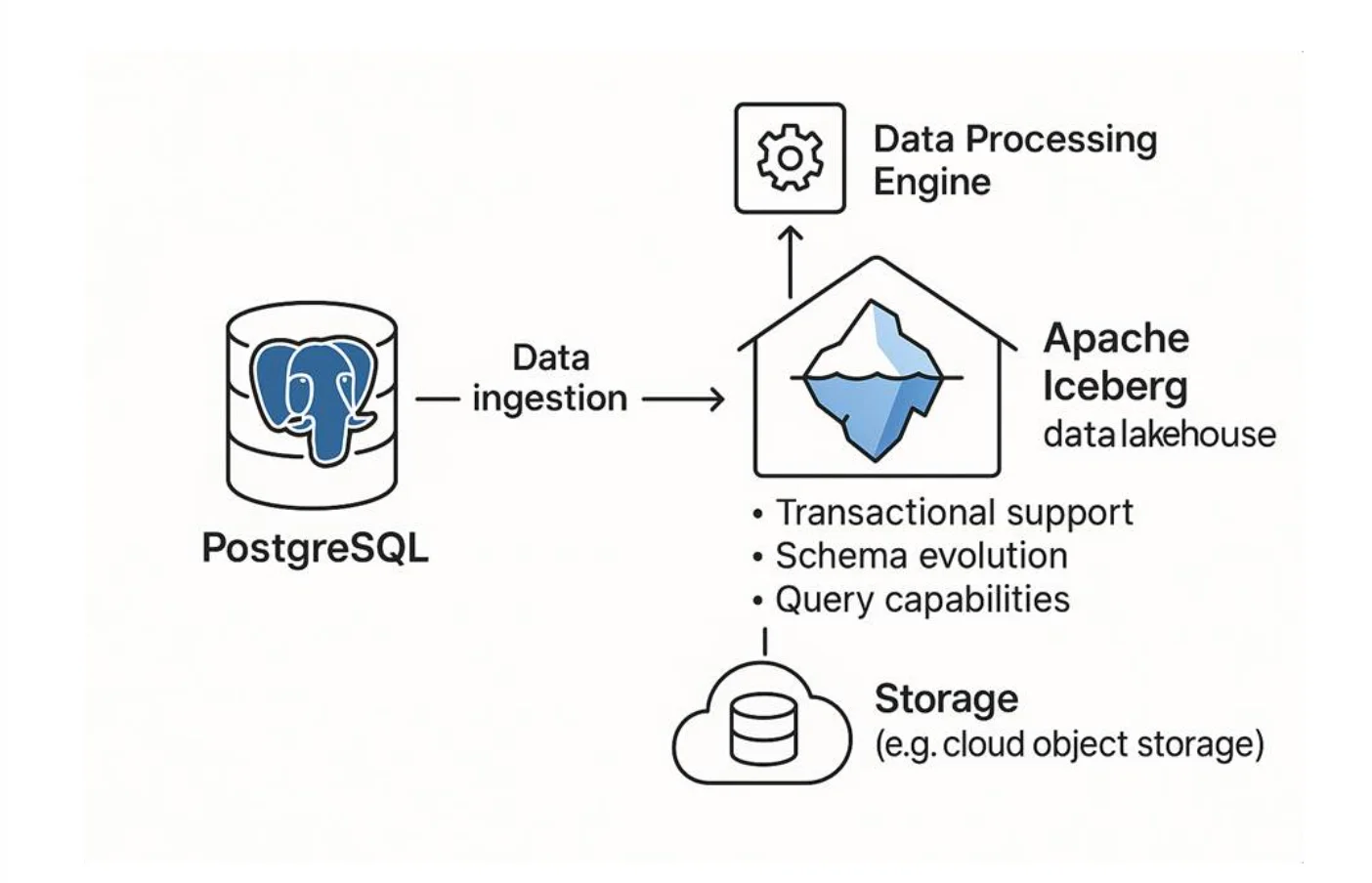
Why PostgreSQL to Iceberg Replication is Essential for Modern Data Teams
Unlock Scalable Real-Time Analytics Without Production Impact
Replicating PostgreSQL to Apache Iceberg transforms how organizations handle operational data analytics by providing several critical advantages:
Cost-Effective Analytics & Business Intelligence: Execute complex analytical queries on live operational data without putting stress on your production PostgreSQL instance, dramatically reducing infrastructure costs compared to traditional data warehouse solutions.
Near Real-Time Reporting Capabilities: Keep your dashboards, reports, and analytics fresh with near real-time data synchronization, enabling faster decision-making and more responsive business operations.
Future-Proof Data Lakehouse Architecture: Embrace open, vendor-agnostic formats like Apache Iceberg to build a modern data lakehouse that avoids vendor lock-in while providing warehouse-like capabilities.
Traditional CDC pipelines that feed cloud data warehouses often become expensive, rigid, and difficult to manage when dealing with schema changes. With Postgres-to-Iceberg replication, you can decouple storage from compute, allowing you to:
- Choose the optimal compute engine for specific workloads (Trino, Spark, DuckDB, etc.)
- Store data once in cost-effective object storage and access it from anywhere
- Eliminate vendor lock-in while reducing overall warehouse expenses
- Support both batch and streaming data ingestion patterns
This replication strategy represents a smart evolution toward an open, efficient data platform that scales with your organization's growth.
Understanding Key Challenges in PostgreSQL to Iceberg Replication
While the benefits are compelling, implementing reliable PostgreSQL to Iceberg CDC replication presents several technical hurdles that require careful planning:
Change Data Capture Implementation Complexity
Real-time vs. batch replication significantly impacts both data freshness and infrastructure complexity. Real-time CDC offers low-latency updates but requires more sophisticated setup and monitoring, while batch replication simplifies management at the cost of data latency.
Schema Evolution and Data Type Mapping
PostgreSQL's flexible data types can clash with Iceberg's stricter type system, making schema evolution management crucial for long-term success. Careful mapping strategies and backward compatibility considerations are essential to prevent data pipeline failures.
Performance Optimization and Cost Management
Frequent, small writes—especially common with real-time CDC streams—can lead to metadata bloat and increased storage costs. Implementing proper compaction strategies and optimized write patterns becomes critical for maintaining performance and controlling expenses.
Data Consistency and Ordering Guarantees
Establishing reliable PostgreSQL logical replication pipelines, particularly during initial full loads, presents challenges around missing or duplicate events that can compromise data quality. Tools that provide at-least-once delivery guarantees, combined with deduplication and idempotent write strategies, are essential safeguards.
Metadata Management and Partitioning Strategy
Apache Iceberg relies on robust metadata management for query performance optimization. Poor partitioning schemes, missing statistics, or inadequate compaction processes can significantly degrade query performance and increase operational costs.
Step-by-Step Guide: PostgreSQL to Iceberg Replication with OLake
Prerequisites for Setting Up Your Replication Pipeline
Before beginning your PostgreSQL to Apache Iceberg migration, ensure you have the following components configured:
- Access to a PostgreSQL database with WAL (Write-Ahead Logging) enabled for CDC
- AWS Glue Catalog setup for Iceberg metadata management
- S3 bucket configured for Iceberg table data storage
- OLake UI deployed (locally or in your cloud environment)
- Docker, PostgreSQL credentials, and AWS S3 access configured
- Apache Iceberg and Catalog configuration credentials
For this guide, we'll use AWS Glue catalog for Apache Iceberg and S3 as the primary object store, though OLake supports multiple catalog options including Nessie, Polaris, Hive, and Unity.
Step 1: Configure PostgreSQL for Logical Replication
OLake offers both JDBC-based Full Refresh and Bookmark-based Incremental sync modes, so if you don't have permissions to create replication slots, you can start syncing immediately with standard database credentials.
However, for real-time CDC capabilities, you'll need to enable logical replication in PostgreSQL using these SQL commands:
Enable Logical Replication Settings
Instead of manually modifying postgresql.conf, use SQL commands to apply runtime settings:
-- Enable logical WAL level for CDC
ALTER SYSTEM SET wal_level = 'logical';
-- Configure replication slots and senders
ALTER SYSTEM SET max_replication_slots = 4;
ALTER SYSTEM SET max_wal_senders = 4;
-- Apply configuration changes
SELECT pg_reload_conf();
Important Note: Cloud-hosted databases (like Amazon RDS or Google Cloud SQL) may require modifying these settings through the provider's console or parameter groups.
Grant Replication Permissions
If using a dedicated role for OLake (e.g., "olake_user"), ensure proper privileges:
ALTER ROLE olake_user WITH REPLICATION;
Alternatively, you can use any existing superuser or role with replication permissions.
Create Publication and Logical Replication Slot
OLake captures changes through a logical replication slot with pgoutput and requires a publication:
CREATE PUBLICATION olake_publication FOR ALL TABLES WITH (publish = 'insert,update,delete,truncate');
SELECT * FROM pg_create_logical_replication_slot('olake_slot', 'pgoutput');
This begins tracking changes from the current WAL position. Ensure the publication name matches your OLake source configuration.
Step 2: Deploy and Configure OLake UI
OLake UI provides a web-based interface for managing replication jobs, data sources, destinations, and monitoring without requiring command-line interaction.
Quick Start Installation
To install OLake UI using Docker and Docker Compose:
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose.yml | docker compose -f - up -d
Access and Initial Setup
- Access OLake UI at: http://localhost:8000
- Default login credentials: admin / password
- Complete setup documentation: OLake UI Getting Started Guide
Alternative: OLake also provides a configurable CLI for advanced users who prefer command-line operations. CLI documentation is available at: OLake CLI Guide.
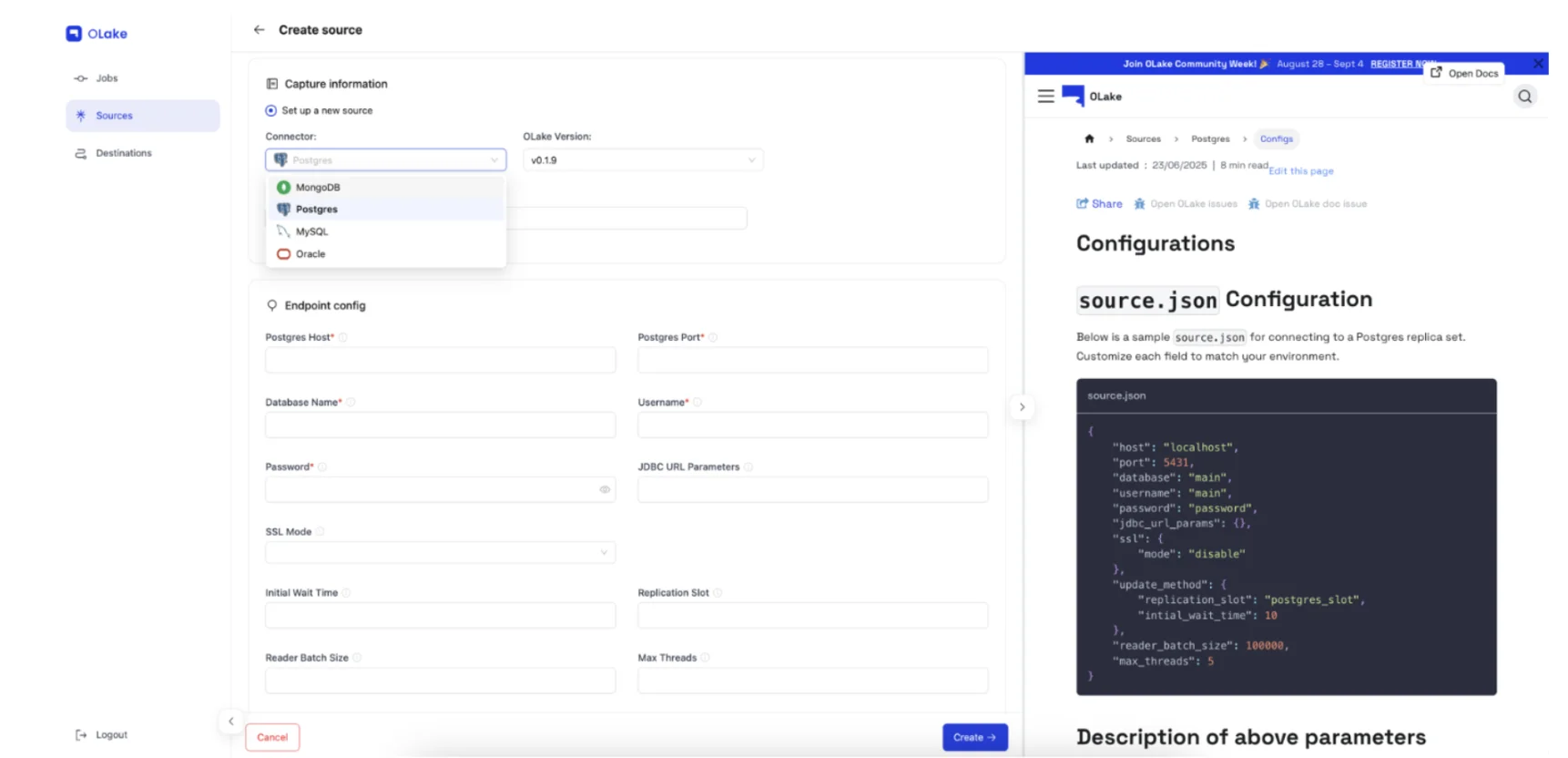
Step 3: Configure PostgreSQL Source Connection
In the OLake UI interface:
- Navigate to Sources → Add Source → Postgres
- Enter your PostgreSQL connection details:
- Host and port information
- Username and password credentials
- Database name
- OLake automatically detects optimal chunking strategies for PostgreSQL (using CTID or batch splits for high-throughput scenarios)
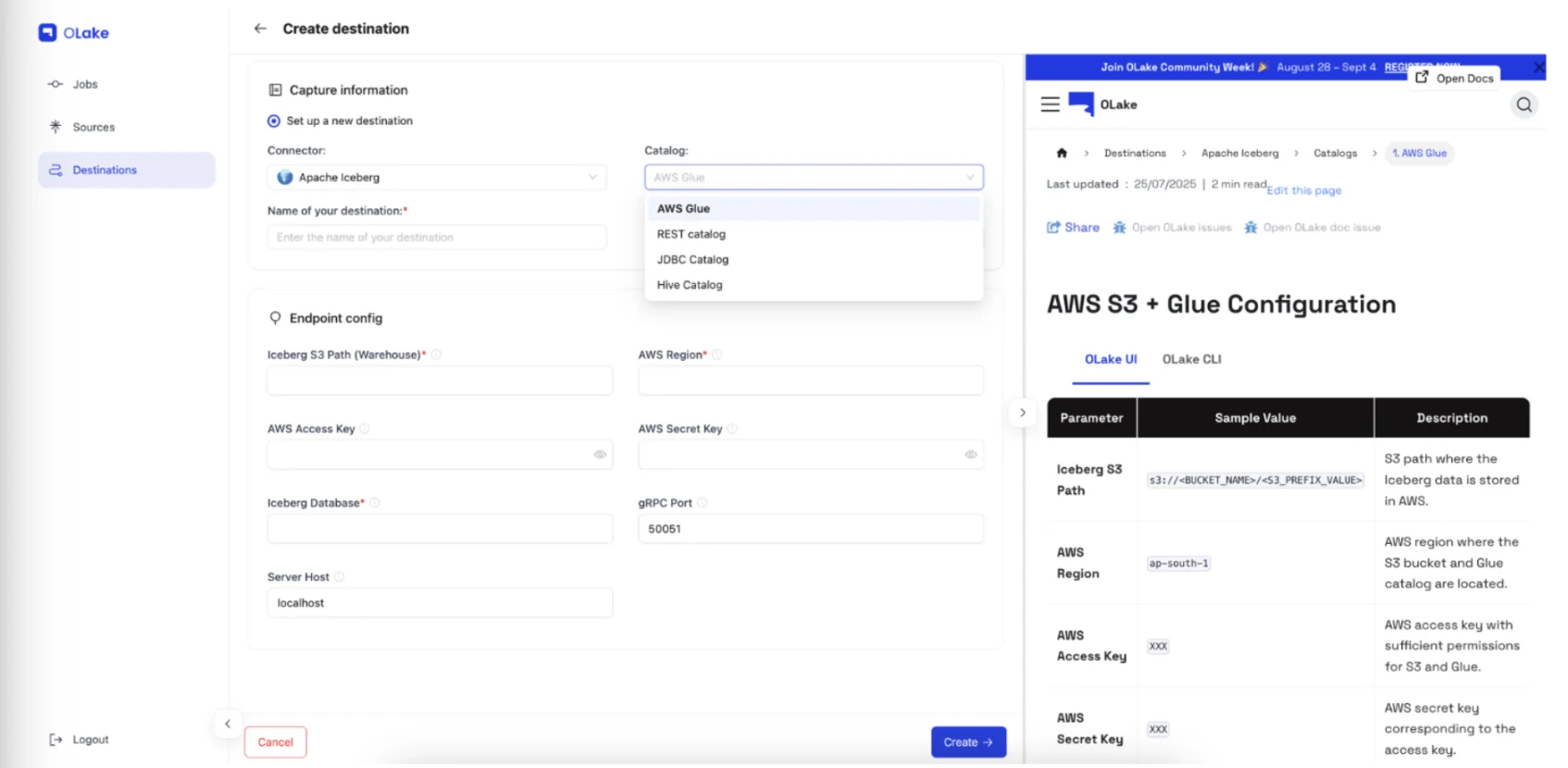
Step 4: Set Up Iceberg Destination with AWS Glue
Configure your Apache Iceberg destination in the OLake UI:
- Navigate to Destinations → Add Destination → Glue Catalog
- Enter AWS Glue configuration:
- AWS region for Glue catalog
- IAM credentials (optional if your instance has appropriate IAM roles)
- S3 bucket selection for Iceberg table storage
OLake supports multiple Iceberg catalog implementations including Glue, Nessie, Polaris, Hive, and Unity Catalog. For detailed configuration of other catalogs, refer to the Catalog Compatibility Overview.
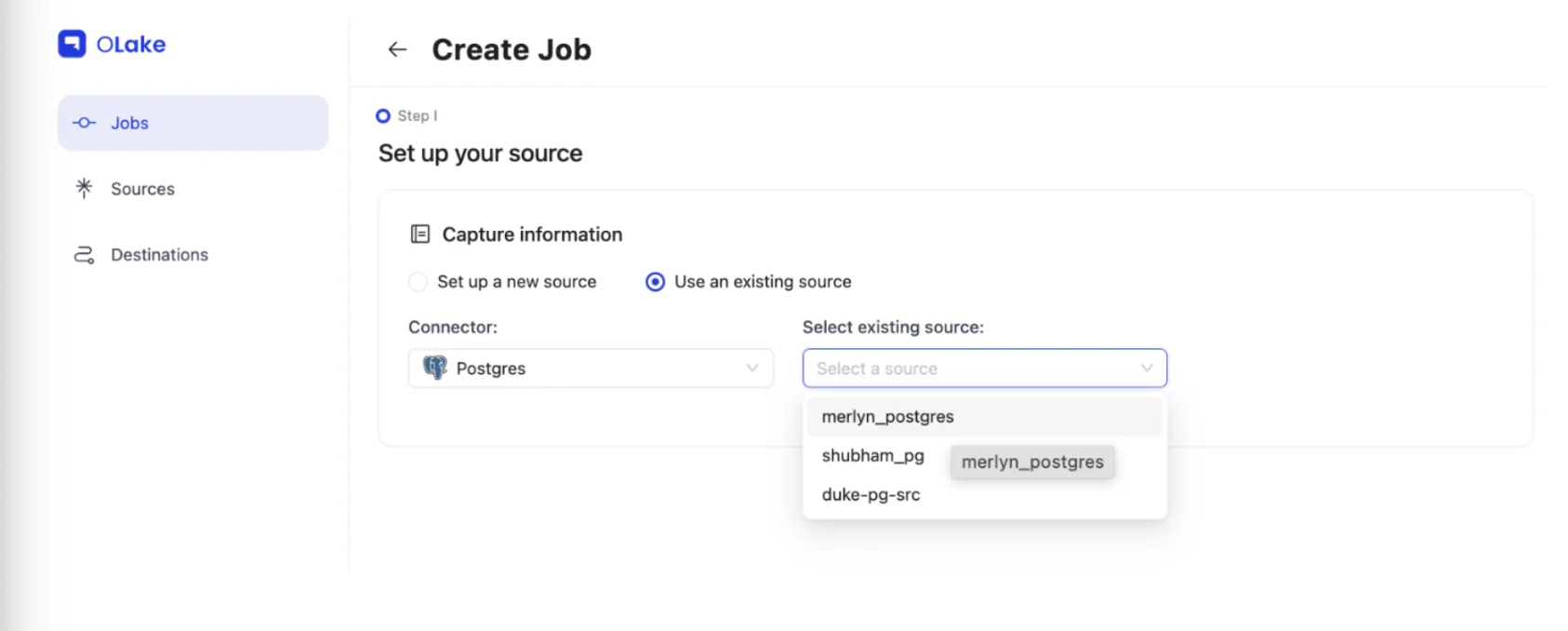
Step 5: Create and Configure Your Replication Job
Once source and destination connections are established:
- Navigate to the Jobs section and create a new job
- Configure job settings:
- Add descriptive job name
- Set replication frequency/schedule
- Select your existing source and destination configurations
- In the schema section, choose tables/streams for Iceberg synchronization
Choose Synchronization Mode
For each stream, select the appropriate sync mode based on your requirements:
- Full Refresh: Complete data sync on every job execution
- Full Refresh + Incremental: Initial full backfill followed by incremental updates based on bookmark columns (e.g., "updated_at")
- Full Refresh + CDC: Initial full backfill followed by real-time CDC based on WAL logs
- CDC Only: Stream only new changes from current WAL log position
Advanced Configuration Options
- Normalization: Disable for raw JSON data storage
- Partitioning: Configure regex patterns for Iceberg table partitioning
- Detailed partitioning strategies: Iceberg Partitioning Guide
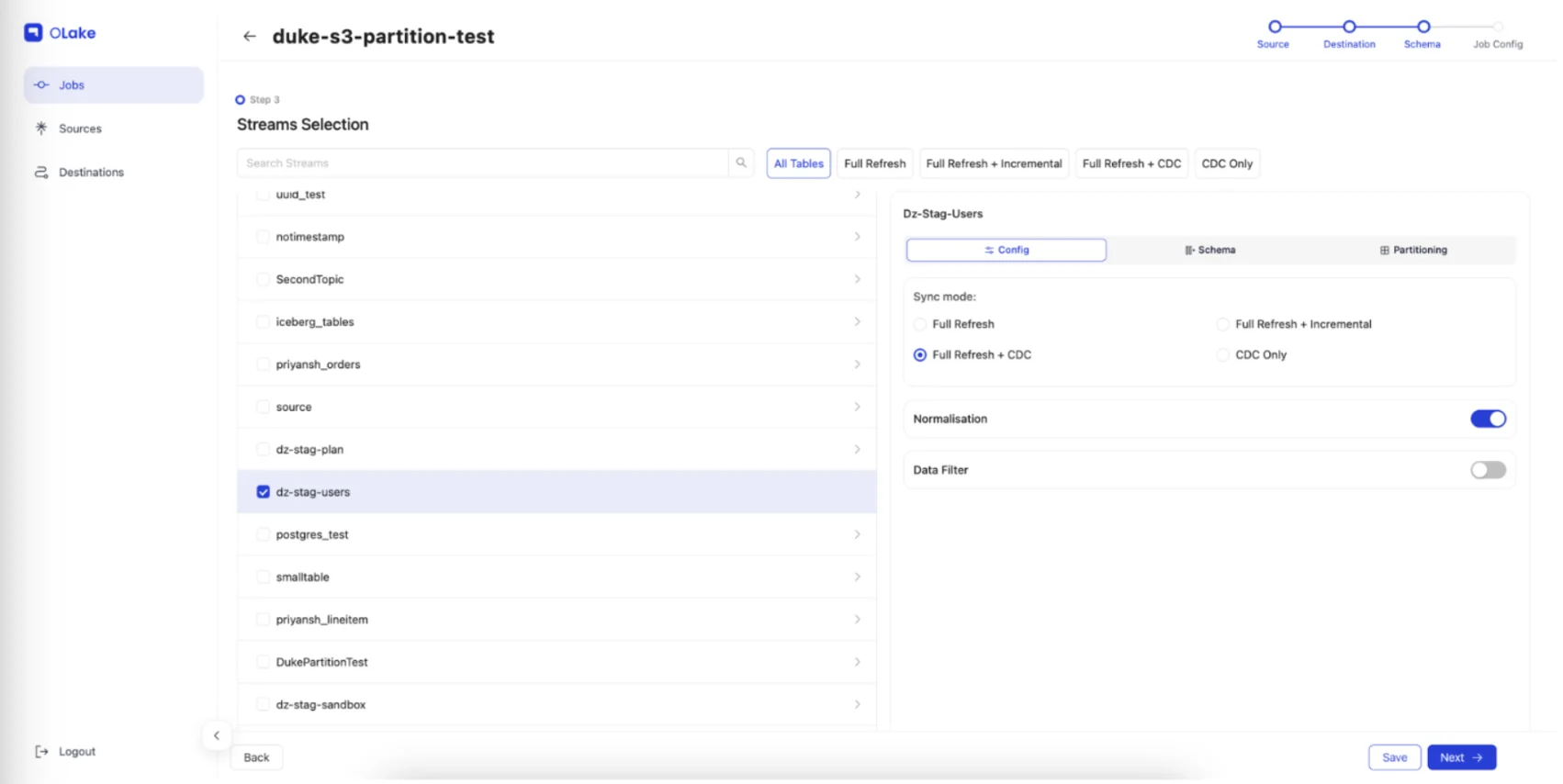
Step 6: Execute Your Synchronization
After saving your job configuration:
- Use "Sync Now" for immediate execution
- Or wait for scheduled execution based on configured frequency
Important: Ordering during initial full loads is not guaranteed. If data ordering is critical for downstream consumption, handle sorting requirements during query time or in downstream processing.
Iceberg Database Structure in S3
Your replicated data creates a structured hierarchy in S3:
s3://your-bucket/
└── database_name.db/
├── table1/
│ ├── data/ (Parquet files)
│ └── metadata/ (JSON and Avro files)
├── table2/
│ ├── data/
│ └── metadata/
└── ...
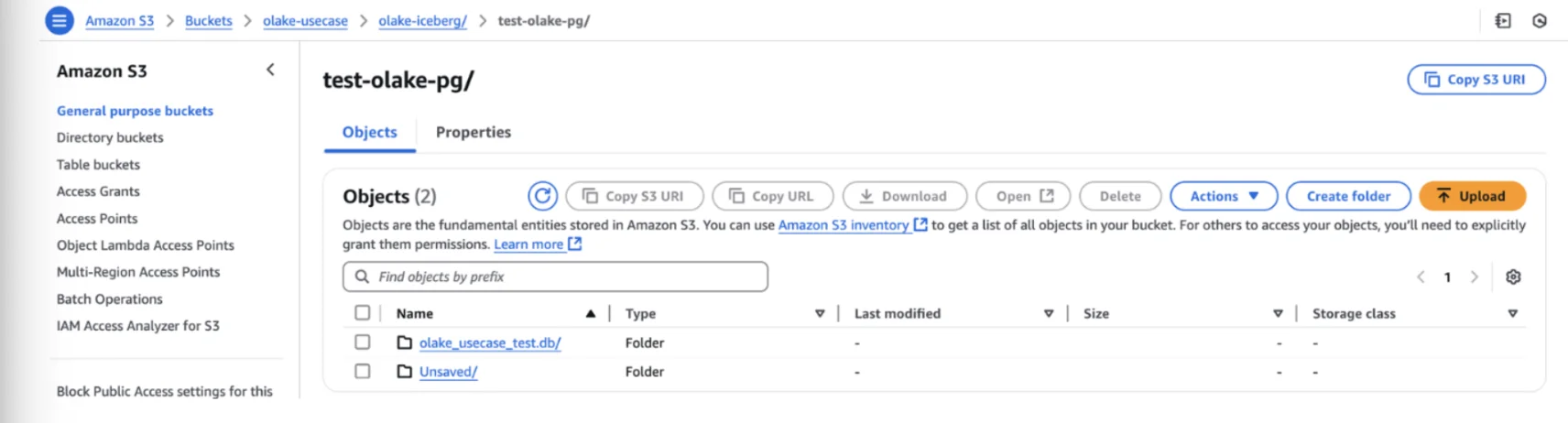
By default, OLake stores data files as Parquet format with metadata in JSON and Avro formats, following Apache Iceberg specifications.
Step 7 (Optional): Query Iceberg Tables with AWS Athena
To validate your replication setup, configure AWS Athena for querying your Iceberg database:
- Set up Athena to connect to your Glue catalog
- Execute SQL queries against your replicated Iceberg tables
- Verify data consistency and query performance
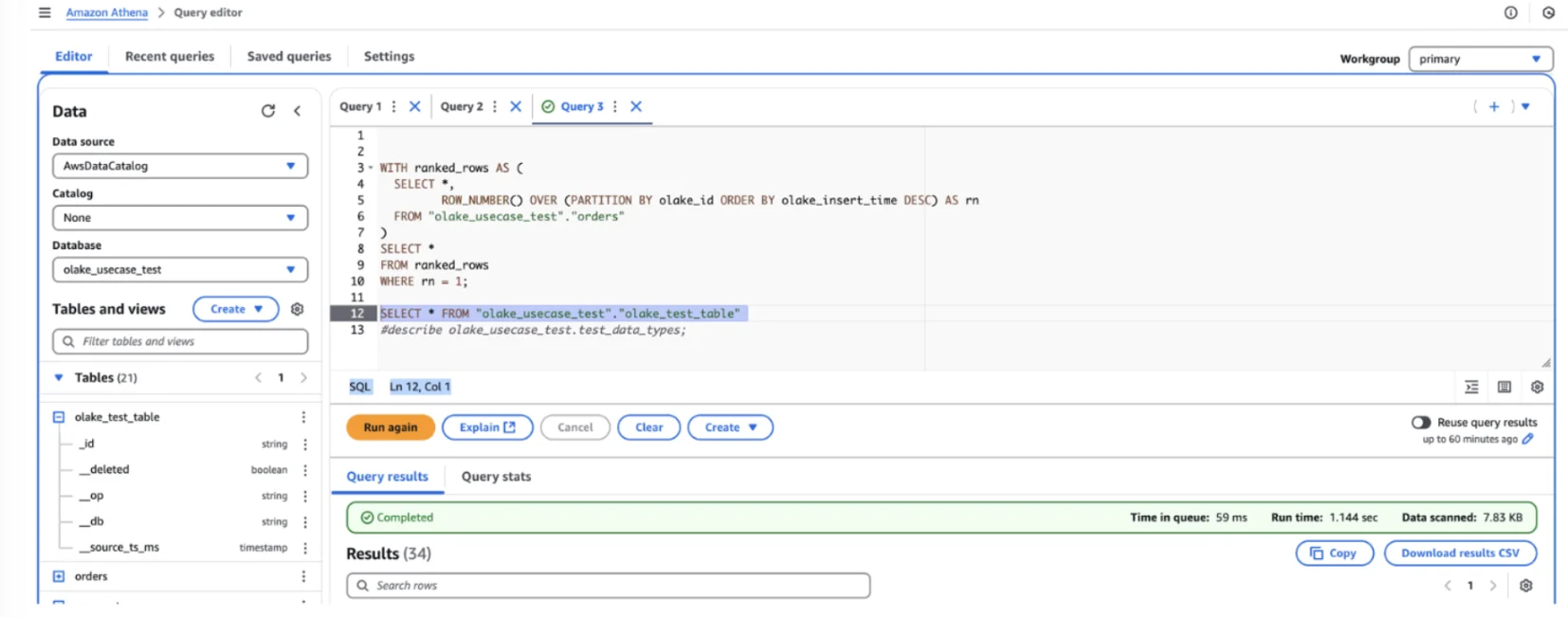
Production-Ready Best Practices for PostgreSQL to Iceberg Replication
Before deploying your PostgreSQL to Iceberg CDC pipeline to production, implement these critical optimization strategies:
Ensure Data Integrity with Primary Keys
Primary keys are essential for accurate deduplication and CDC processing. OLake relies on primary keys to differentiate between updates and inserts, which becomes critical when handling out-of-order events or recovery scenarios.
Implement Smart Partitioning Strategies
Choose partition columns based on actual query patterns and data volume characteristics:
- Temporal partitioning: Use created_at or updated_at for event tables and time-series data
- Dimensional partitioning: Implement customer_id or region for lookup and dimensional data
- Hybrid approaches: Combine temporal and dimensional partitioning for complex analytical workloads
Poor partitioning choices directly impact query performance and file scan costs, making this optimization crucial for long-term success.
Automate Compaction Processes
Frequent small CDC writes create numerous tiny files, leading to the "small file problem" that degrades query performance. Implement automated compaction jobs to:
- Merge small files into larger, more efficient structures
- Optimize metadata overhead and reduce storage costs
- Minimize read overhead in Iceberg-compatible engines like Trino, Spark, and DuckDB
Monitor Replication Lag and Performance
Establish comprehensive monitoring for replication slot lag and sync timestamps to detect issues early. Large lag periods may indicate:
- Backpressure in your replication pipeline
- PostgreSQL WAL bloat requiring attention
- Network connectivity or performance issues
- Resource constraints on source or destination systems
Maintain State Backups and Recovery Procedures
The state.json file serves as the single source of truth for replication progress tracking. Implement regular backups to prevent:
- Accidental replication resets during maintenance
- Data loss during disaster recovery scenarios
- Manual recovery efforts that could introduce data inconsistencies
Advanced Optimization Techniques
Leverage Multiple Compute Engines
One of the key advantages of Apache Iceberg's open format is compatibility with multiple query engines. Optimize your analytical workloads by:
- Using Apache Spark for large-scale batch processing and complex transformations
- Implementing Trino for interactive analytics and ad-hoc queries
- Deploying DuckDB for fast analytical queries on smaller datasets
- Integrating with AWS Athena for serverless SQL analytics
Implement Schema Evolution Strategies
Plan for schema evolution requirements from the beginning:
- Test schema changes in development environments first
- Implement backward-compatible schema modifications when possible
- Use Iceberg's built-in schema evolution features for seamless updates
- Document schema change procedures for your team
Optimize for Different Workload Patterns
Configure your pipeline based on specific analytical workload requirements:
- Real-time dashboards: Prioritize low-latency CDC with frequent small updates
- Batch analytics: Focus on efficient bulk processing with optimized file sizes
- Mixed workloads: Balance real-time capabilities with batch optimization needs
- Machine learning pipelines: Ensure consistent data formats and feature engineering support
Conclusion: Building Your Modern Data Analytics Platform
Replicating PostgreSQL to Apache Iceberg provides the foundation for a modern, flexible data lakehouse architecture without the constraints and costs of traditional warehouse solutions. This approach enables organizations to:
- Maintain operational database performance while enabling sophisticated analytics
- Reduce infrastructure costs through efficient storage and compute separation
- Future-proof data architecture with open, vendor-agnostic formats
- Scale analytics capabilities without impacting production systems
With OLake, you gain access to:
- Seamless full and incremental synchronization with minimal configuration overhead
- Comprehensive schema evolution support for multiple tables and data types
- Open file format compatibility that integrates with your preferred query engines and tools
- Production-ready monitoring and management capabilities for enterprise deployments
The combination of PostgreSQL's reliability as an operational database and Apache Iceberg's analytical capabilities creates a powerful foundation for data-driven decision making. Whether you're building real-time dashboards, implementing advanced analytics, or developing machine learning pipelines, this replication strategy provides the scalability and flexibility modern organizations require.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the difference between PostgreSQL and Apache Iceberg?
PostgreSQL is an OLTP database designed for transactional application workloads with fast row-based operations. Apache Iceberg is an open table format optimized for large-scale analytics with columnar storage, built for data lakes rather than operational databases.
How does PostgreSQL logical replication work?
PostgreSQL writes all changes to a Write-Ahead Log (WAL). Logical replication reads this WAL using replication slots and publications, streaming INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE operations to downstream systems like Iceberg in real-time without impacting database performance.
Do I need PostgreSQL superuser privileges for CDC?
No! While superuser simplifies setup, you only need specific privileges: REPLICATION permission, and SELECT access on tables you want to replicate. Cloud providers like AWS RDS and Google Cloud SQL support logical replication with limited-privilege accounts.
Can I replicate PostgreSQL without enabling logical replication?
Yes! OLake offers JDBC-based Full Refresh and Bookmark-based Incremental sync modes. If you can't modify WAL settings or create replication slots, you can still replicate data using standard PostgreSQL credentials with timestamp-based incremental updates.
How does OLake handle PostgreSQL schema changes?
OLake automatically detects schema evolution. When you add, drop, or modify columns in PostgreSQL, these changes propagate to Iceberg tables without breaking your pipeline. The state management ensures schema and data stay synchronized.
What happens if my PostgreSQL WAL fills up?
Proper replication slot monitoring is crucial. If OLake falls behind, PostgreSQL retains WAL files until they're consumed. OLake provides lag monitoring and automatic recovery to prevent WAL bloat, but you should set appropriate WAL retention limits.
How do I handle large PostgreSQL databases for initial load?
OLake uses intelligent chunking strategies (CTID-based or batch splits) to load data in parallel without locking tables. A 1TB PostgreSQL database typically loads in 4-8 hours depending on network and storage performance, and the process can be paused/resumed.
What query engines work with PostgreSQL-sourced Iceberg tables?
Any Iceberg-compatible engine: Apache Spark for batch processing, Trino/Presto for interactive queries, DuckDB for fast analytical workloads, AWS Athena for serverless SQL, Snowflake, Databricks, and many others - all querying the same data.
Can I replicate specific PostgreSQL tables or schemas?
Yes! OLake lets you select specific tables, schemas, or even filter rows using SQL WHERE clauses. This selective replication reduces storage costs and improves query performance by replicating only the data you need for analytics.
What's the cost comparison between PostgreSQL RDS and Iceberg on S3?
PostgreSQL RDS storage costs ~$0.115/GB/month plus compute charges that run 24/7. Iceberg on S3 costs ~$0.023/GB/month (5x cheaper) with compute costs only when querying. Organizations typically save 50-75% on analytics infrastructure.
OLake
Achieve 5x speed data replication to Lakehouse format with OLake, our open source platform for efficient, quick and scalable big data ingestion for real-time analytics.
