Overview
The OLake DB2 LUW (Linux Unix Windows) Source connector supports multiple synchronization modes. It offers features like parallel chunking, checkpointing, and automatic resume for failed full loads. This connector can be used within the OLake UI or run locally via Docker for open-source workflows.
Sync Modes Supported
- Full Refresh
- Incremental
Prerequisites
Version Prerequisites
- DB2 Version 11.5.3 or higher.
Connection Prerequisites
- Read access to the tables for the DB2 user.
- IBM Data Server ODBC and CLI driver is not supported for Linux (arm64). Avoid using this machine for DB2 workloads.
- The recommended CPU architecture to run DB2 sync is AMD64.
After initial Prerequisites are fulfilled, the configurations for DB2 can be configured.
Configuration
- Use Olake UI for DB2
- Use Olake CLI for DB2
1. Navigate to the Source Configuration Page
- Complete the OLake UI Setup Guide
- After logging in to the OLake UI, select the
Sourcestab from the left sidebar. - Click
Create Sourceon the top right corner. - Select DB2 from the connector dropdown.
- Provide a name for this source.
2. Provide Configuration Details
- Enter DB2 credentials.
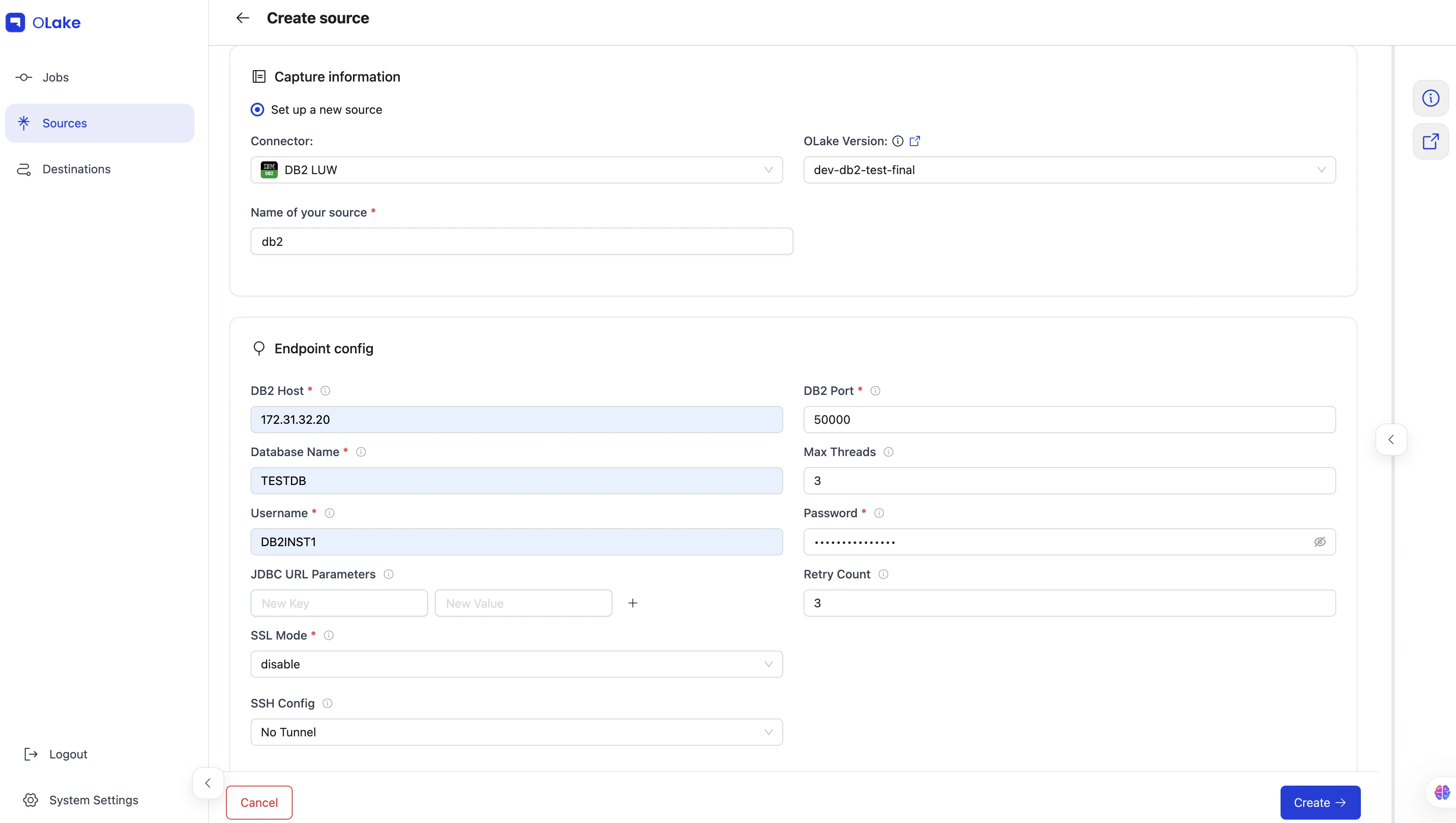
| Field | Description | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
DB2 Host required | Hostname or IP address of the DB2 database server. | DB2 LUW-host |
DB2 Port required | TCP port on which the DB2 listener is accepting connections. | 50000 |
Database Name required | The name of the target database to connect to. | olake-db |
Password required | The password corresponding to the provided username for authentication. | db2pwd |
Username required | Database user used to authenticate the connection. | db2-user |
| Max Threads | Maximum number of worker threads the connector can spin up for parallel tasks. | 10 |
| JDBC URL Parameters | Extra JDBC URL parameters for fine-tuning the connection. | {"connectTimeout":"20"} |
| SSL Mode | SSL configuration for the database connection. Contains details such as the SSL mode. | disable |
| SSH Config | Configure OLake to connect through an SSH tunnel. See SSH Config details for the list of supported parameters. |
|
| Retry Count | Number of times the retry will take place incase of timeout before failing the sync. | 3 |
3. Test Connection
-
Once the connection is validated, the DB2 source is created. Jobs can then be configured using this source.
-
In case of connection failure, refer to the Troubleshooting section.
1. Create Configuration File
- Once the OLake CLI is setup, create a folder to store configuration files such as
source.jsonanddestination.json.
The source.json file for DB2 must contain these mandatory fields.
2. Provide Configuration Details
An example source.json file will look like this:
{
"host": "DB2 LUW-host",
"port": 50000,
"database": "DB2 LUW-DBName",
"username": "DB2 LUW-Username",
"password": "DB2 LUW-Password",
"ssl": {
"mode": "disable"
},
"max_threads": 30,
"jdbc_url_params": {},
"retry_count": 3
}
| Field | Description | Example Value | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
DB2 Host required | Hostname or IP address of the DB2 database server. | DB2 LUW-host | String |
DB2 Port required | TCP port on which the DB2 listener is accepting connections. | 50000 | Integer |
Database Name required | The name of the target database to connect to. | olake-db | String |
Password required | The password corresponding to the provided username for authentication. | db2pwd | String |
Username required | Database user used to authenticate the connection. | db2-user | String |
| Max Threads | Maximum number of worker threads the connector can spin up for parallel tasks. | 10 | Integer |
| JDBC URL Parameters | Extra JDBC URL parameters for fine-tuning the connection. | {"connectTimeout":"20"} | Object |
| SSL Mode | SSL configuration for the database connection. Contains details such as the SSL mode. | disable | Object |
| SSH Config | Configure OLake to connect through an SSH tunnel. See SSH Config details for the list of supported parameters. |
| Object |
| Retry Count | Number of times the retry will take place incase of timeout before failing the sync. | 3 | Integer |
Similarly, destination.json file can be created inside this folder. For more information, see destination documentation.
3. Check Source Connection
To verify the database connection following command needs to be run:
docker run --pull=always \
-v "[PATH_OF_CONFIG_FOLDER]:/mnt/config" \
olakego/source-db2:latest \
check \
--config /mnt/config/source.json
When you run any OLake commands using .buildsh, the IBM Data Server ODBC and CLI driver gets automatically installed on your system.
-
If OLake is able to connect with DB2
{"connectionStatus":{"status":"SUCCEEDED"},"type":"CONNECTION_STATUS"}response is returned. -
In case of connection failure, refer to the Troubleshooting section.
Data Type Mapping
| DB2 Data Types | Destination Data Type |
|---|---|
| SMALLINT, INTEGER | int |
| BIGINT | bigint |
| REAL | float |
| FLOAT, NUMERIC, DOUBLE, DECIMAL, DECFLOAT | double |
| CHAR, CHARACTER, VARCHAR, LONG, CLOB, GRAPHIC, VARGRAPHIC, LONG VARGRAPHIC, XML, ARRAY, ROW, BLOB, DBCLOB, TIME | string |
| BOOLEAN | boolean |
| DATE, TIMESTAMP | timestamp |
- OLake always ingests timestamp data in UTC format, independent of the source timezone.
- Run this command to collect table and index statistics. This populates the system catalog tables with metadata such as npages, page size, and average row size, which OLake requires during sync:
CALL SYSPROC.ADMIN_CMD('RUNSTATS ON TABLE schema_name.table_name AND INDEXES ALL');
For information on how to provide the proper timestamp format for DB2 when filtering data, please refer to the Data Filter section.
Date and Time Handling
During transfer, values in date, time, and timestamp columns are modified to ensure valid calendar ranges and destination compatibility.
- Case I (Year 0000):
Source dates with year0000are not valid in most destinations, so we change them to the epoch start date.
Example:0000-05-10 → 1970-01-01 - Case II (Year > 9999):
Extremely large years are capped at9999. The month and date are not affected.
Examples:10000-03-12 → 9999-03-12 - Case III (Invalid month/day):
When the month or day exceeds valid ranges (i.e. month > 12 or day > 31), or the combined date is invalid, the value is replaced with the epoch start date.
Examples:2024-13-15 → 1970-01-01,2023-04-31 → 1970-01-01
These rules apply to date, time, and timestamp columns during transfer.
Troubleshooting
1. ALTER TABLE in DB2 LUW
In DB2 LUW, certain ALTER TABLE operations can place a table in REORG PENDING state, and while in this state:
- Queries, inserts, or sync jobs may fail with errors like SQL0668N.
- A
REORG TABLEis required before normal access is restored.
Operations that commonly cause this include:
ADD COLUMNDROP COLUMNALTER COLUMN(datatype/length changes)- Some changes to row organization or table attributes
Required fix: Running a reorganization is the correct resolution:
CALL SYSPROC.ADMIN_CMD('REORG TABLE schema_name.table_name');
This clears the REORG PENDING state and makes the table usable again.