Overview
The OLake Kafka Source connector syncs messages from Kafka topics directly to the destination. It supports only one synchronization mode and offers features like parallel partition processing and checkpointing. This connector can be used within the OLake UI or run locally via Docker for open-source workflows.
Kafka topics have a configured retention period. Once messages exceed this retention period, they are automatically deleted from the topic. OLake cannot access or sync deleted messages. Ensure your sync schedule runs frequently enough to capture data before it expires.
Kafka Connector Requirements
- Kafka as a source connector is available in OLake v0.3.0 and above on both the source and destination side.
- The OLake Kafka connector has been tested specifically with Amazon MSK (Amazon Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka), AWS's fully managed Apache Kafka service. The connector uses standard Kafka protocols and should work with other Kafka distributions.
Authentication
OLake supports three authentication methods for connecting to Kafka brokers:
1. PLAINTEXT
No authentication or encryption. Suitable only for development or testing environments where security is not a concern.
- Security Protocol:
PLAINTEXT - Configuration: No additional authentication parameters required
2. SASL_PLAINTEXT
Authentication without encryption. Credentials are verified, but data is transmitted in plaintext.
- Security Protocol:
SASL_PLAINTEXT - Supported SASL Mechanisms:
- PLAIN: Simple username/password authentication
- SCRAM-SHA-512: Salted Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism with SHA-512 hashing
Example Configuration:
"protocol": {
"security_protocol": "SASL_PLAINTEXT",
"sasl_mechanism": "SCRAM-SHA-512",
"sasl_jaas_config": "org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username=\"YOUR_USERNAME\" password=\"YOUR_PASSWORD\";"
}
3. SASL_SSL
Authentication with SSL/TLS encryption. This is the most secure option, providing both authentication and encrypted communication.
- Security Protocol:
SASL_SSL - Supported SASL Mechanisms:
- PLAIN: Simple username/password authentication over SSL
- SCRAM-SHA-512: Salted Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism with SHA-512 hashing over SSL
Example Configuration:
"protocol": {
"security_protocol": "SASL_SSL",
"sasl_mechanism": "SCRAM-SHA-512",
"sasl_jaas_config": "org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username=\"YOUR_USERNAME\" password=\"YOUR_PASSWORD\";"
}
Prerequisites
Version Prerequisites
Kafka Version 0.10.1.0 or higher.
Connection Prerequisites
- OLake and the Kafka broker servers must be accessible within the same network.
After initial Prerequisites are fulfilled, the configurations for Kafka can be configured.
Configuration
- Use Olake UI for Kafka
- Use OLake CLI for Kafka
1. Navigate to the Source Configuration Page
- Complete the OLake UI Setup Guide
- After logging in to the OLake UI, select the
Sourcestab from the left sidebar. - Click
Create Sourceon the top right corner. - Select Kafka from the connector dropdown
- Provide a name for this source.
2. Provide Configuration Details
-
Enter Kafka credentials.
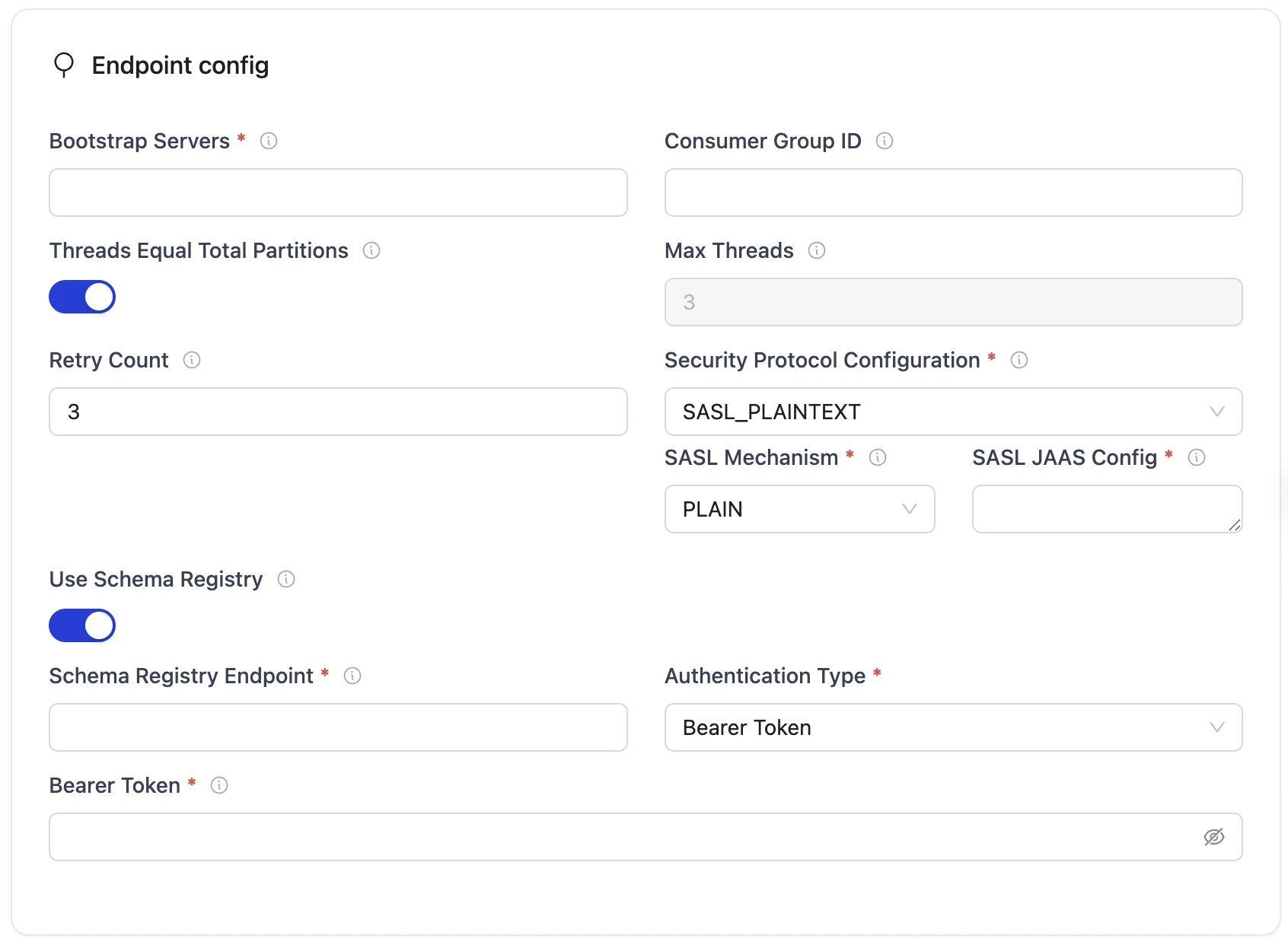
| Field | Description | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
Kafka BootstrapServers required | Comma-separated list of Kafka broker addresses (host:port) for establishing the initial connection to the Kafka cluster. | "broker:9092, broker:9093" |
| Consumer Group ID | Unique identifier for the consumer group used to track messages and coordinate with consumer members. If not provided, OLake automatically generates one. | example-consumer-group |
Protocol required | Configuration object containing Kafka security settings and authentication configurations for connecting to Kafka. Sub-parameters: security_protocol, sasl_mechanism, sasl_jaas_config. | { "security_protocol": "SASL_SSL", "sasl_mechanism": "SCRAM-SHA-512", "sasl_jaas_config": "org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username=\"YOUR_KAFKA_USERNAME\" password=\"YOUR_KAFKA_PASSWORD\";"} |
Security Protocol required | Protocol used for communication with Kafka. Supported options: PLAINTEXT, SASL_PLAINTEXT, or SASL_SSL. | SASL_SSL |
| SASL Mechanism | Specifies the type of SASL authentication protocol used to verify client identity when connecting to Kafka. Supported options: PLAIN, SCRAM-SHA-512. | "SCRAM-SHA-512" |
| SASL JAAS Config | JAAS configuration string containing the login module and authentication credentials (username and password) for SASL authentication. | If SASL mechanism is PLAIN: "org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username="username" password="password";" If SASL mechanism is SCRAM-SHA-512: "org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username="username" password="password";" |
| Threads Equal Total Partitions | When true, the number of consumer thread is equal to total number of partitions for most optimal parallel processing. When false, consumer threads are set to the max_threads value. | false |
| Max Threads | Maximum number of parallel threads for processing or syncing data. | 3 |
| Backoff Retry Count | Number of retry attempts for establishing sync with exponential backoff. | 3 |
| Schema Registry Endpoint | Endpoint of the Confluence Schema Registry. For AVRO-based topics, schema registry is mandatory. | http://localhost:8081 |
| Authentication Type | Authentication method for the Schema Registry. Supported options: - No Authentication - Username & Password - Bearer Token | 1. No Authentication - nothing is required 2. Username & Password - username and password is required (e.g., username = dummy, password = password) 3. Bearer Token - bearer token is required (e.g., dummy_token) |
3. Test Connection
-
Once the connection is validated, the Kafka source is created. Jobs can then be configured using this source.
-
In case of connection failure, refer to the Troubleshooting section.
1. Create Configuration File
- Once the OLake CLI is set up, create a folder to store configuration files such as
source.jsonanddestination.json.
The source.json file for Kafka must contain these mandatory fields.
2. Provide Configuration Details
An example source.json file will look like this:
{
"bootstrap_servers": "broker:9092, broker:9093",
"protocol": {
"security_protocol": "SASL_SSL",
"sasl_mechanism": "SCRAM-SHA-512",
"sasl_jaas_config": "org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username=\"YOUR_KAFKA_USERNAME\" password=\"YOUR_KAFKA_PASSWORD\";"
},
"consumer_group_id": "example-consumer-group",
"max_threads": 3,
"threads_equal_total_partitions": false,
"backoff_retry_count": 3,
"schema_registry": {
"endpoint": "http://localhost:8081",
"username": "dummy",
"password": "password"
}
}
| Field | Description | Example Value | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
Kafka BootstrapServers required | Comma-separated list of Kafka broker addresses (host:port) for establishing the initial connection to the Kafka cluster. | "broker:9092, broker:9093" | String |
| Consumer Group ID | Unique identifier for the consumer group used to track message and coordinate with other consumer members. If not provided, OLake automatically generates one. | example-consumer-group | String |
Protocol required | Configuration object containing Kafka security settings and authentication configurations for connecting to Kafka. Sub-parameters: security_protocol, sasl_mechanism, sasl_jaas_config. | { "security_protocol": "SASL_SSL", "sasl_mechanism": "SCRAM-SHA-512", "sasl_jaas_config": "org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username=\"YOUR_KAFKA_USERNAME\" password=\"YOUR_KAFKA_PASSWORD\";"} | Object |
Security Protocol required | Protocol used for communication with Kafka. Supported options: PLAINTEXT, SASL_PLAINTEXT, or SASL_SSL. | "SASL_SSL" | String |
| SASL Mechanism | Specifies the type of SASL authentication protocol used to verify client identity when connecting to Kafka. . Supported options: PLAIN, SCRAM-SHA-512. | "SCRAM-SHA-512" | String |
| SASL JAAS Config | JAAS configuration string containing the login module and authentication credentials (username and password) for SASL authentication. | If SASL mechanism is PLAIN: "org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username="username" password="password";" If SASL mechanism is SCRAM-SHA-512: "org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username="username" password="password";" | String |
| Threads Equal Total Partitions | When true, the number of consumer thread is equal to total number of partitions for most optimal parallel processing. When false, consumer threads are set to the max_threads value. | false | Boolean |
| Max Threads | Maximum number of parallel threads for processing or syncing data. | 3 | Integer |
| Backoff Retry Count | Number of retry attempts for establishing sync with exponential backoff. | 3 | Integer |
| Schema Registry (Optional) | If schema registry is configured, at least schema registry endpoint has to be provided. If authentication is also present, then either authenticate using username and password or bearer_token. For AVRO-based topics, schema registry is mandatory. | "schema_registry": { "endpoint": "http://localhost:8081", "username": "dummy", "password": "dummy-password"} | Object |
Similarly, destination.json file can be created inside this folder. For more information, see destination documentation.
3. Check Source Connection
To verify the database connection following command needs to be run:
docker run --pull=always \
-v "[PATH_OF_CONFIG_FOLDER]:/mnt/config" \
olakego/source-kafka:latest \
check \
--config /mnt/config/source.json
-
If OLake is able to connect with Kafka
{"connectionStatus":{"status":"SUCCEEDED"},"type":"CONNECTION_STATUS"}response is returned. -
In case of connection failure, refer to the Troubleshooting section.
Kafka General Information
When OLake syncs data from Kafka topics to Iceberg, it transfers the complete message structure along with Kafka metadata. This ensures full traceability and context for each message.
Columns Transferred
The following columns are automatically included when syncing Kafka messages to the destination:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| _kafka_key | The key of the message. |
| _kafka_offset | The sequential position of the message within its partition. Guarantees message ordering within a partition. |
| _kafka_partition | The Kafka partition number where the message resides. Used for parallel processing and data distribution. |
| _kafka_timestamp | The timestamp when the message was produced or appended to the Kafka topic. |
- The Kafka messages must contain data in JSON or AVRO format.
- If messages are null or empty, OLake will read the messages but skip writing them to the destination. For AVRO format, a Confluence Schema Registry must be configured—schema registry is mandatory only for AVRO data and if not provided OLake will consider the messages as JSON format.
Normalization
OLake provides flexibility in how message values are stored:
-
Normalization =
true: The payload in thevaluecolumn is Level 0 flattened, and each nested field becomes a separate column in the destination table. This makes querying individual fields easier. -
Normalization =
false: The payload is stored as-is in thevaluecolumn without flattening. The entire JSON object remains in a single column.
Troubleshooting
1. Consumer Group Corruption
If a consumer group becomes corrupted, you'll need to use a different consumer group to continue syncing data. The resolution depends on how you're running OLake.
Using OLake UI
Consumer group names cannot be modified once set in the OLake UI. To resolve a corrupted consumer group, create a new job with a different consumer group ID.
Using OLake CLI
When using the CLI, you can modify the consumer group in your configuration file:
- Open your
source.jsonfile - Update the
consumer_group_idfield with a new consumer group name. - Save the file and run the sync command again
The sync will continue with the new consumer group.
If the issue is not listed here, post the query on Slack to get it resolved within a few hours.