Overview
The OLake MSSQL Source connector supports multiple synchronization modes. It offers features like parallel chunking, checkpointing, and automatic resume for failed full loads. This connector can be used within the OLake UI or run locally via Docker for open-source workflows.
Sync Modes Supported
- Full Refresh
- Full Refresh + CDC
- CDC Only
- Full Refresh + Incremental
Prerequisites
Version Prerequisites
- MSSQL Version 2017 or higher.
CDC Prerequisites
To use CDC with OLake, you must enable CDC on both the database and individual tables you want to capture.
Enable CDC on Database
Connect to your SQL Server database using Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio or your preferred client, then run:
USE MY_DB;
EXEC sys.sp_cdc_enable_db;
For hosted cloud provider versions of SQL Server, use these commands instead:
- Amazon RDS:
EXEC msdb.dbo.rds_cdc_enable_db; - Google Cloud SQL:
EXEC msdb.dbo.gcloudsql_cdc_enable_db;
Enable CDC on Tables
After enabling CDC on the database, enable it on each table you want to capture changes from:
EXEC sys.sp_cdc_enable_table
@source_schema = 'schema_name',
@source_name = 'my_table',
@role_name = 'my_role',
@capture_instance = 'dbo_my_table';
@source_schema: The schema name (typically'dbo')@source_name: The table name@role_name: The database role that controls access to the change data@capture_instance: Optional name for the CDC capture instance (defaults to schema_table if not specified)
In SQL Server, any schema evolution to the source table will not automatically cause it to be added to the CDC change table. The solution is to create a new capture instance which reflects the new state of the source table.
The connector will automatically detect the existence of a second capture instance and will seamlessly switch over to the newest one as soon as it reaches a point in the event stream where they are both valid.
After performing a schema evolution, make sure to create a new capture instance:
EXEC sys.sp_cdc_enable_table
@source_schema = 'schema_name',
@source_name = 'my_table',
@role_name = 'my_role',
@capture_instance = 'dbo_my_table'; --Make sure to give a new name to the capture instance different from the old one.
CDC Limitations
- Columnstore indexes: CDC cannot be enabled on tables with a clustered columnstore index. Starting with SQL Server 2016, it can be enabled on tables with a nonclustered columnstore index.
- Computed columns: CDC doesn't support values for computed columns, even if defined as persisted. Computed columns included in a capture instance will always have a value of
NULL. This is intended behavior, not a bug.
Connection Prerequisites
- Read access to the tables for the MSSQL user.
After initial Prerequisites are fulfilled, the configurations for MSSQL can be configured.
Configuration
- Use Olake UI for MSSQL
- Use OLake CLI for MSSQL
1. Navigate to the Source Configuration Page
- Complete the OLake UI Setup Guide
- After logging in to the OLake UI, select the
Sourcestab from the left sidebar. - Click
Create Sourceon the top right corner. - Select MSSQL from the connector dropdown
- Provide a name for this source.
2. Provide Configuration Details
- Enter MSSQL credentials.
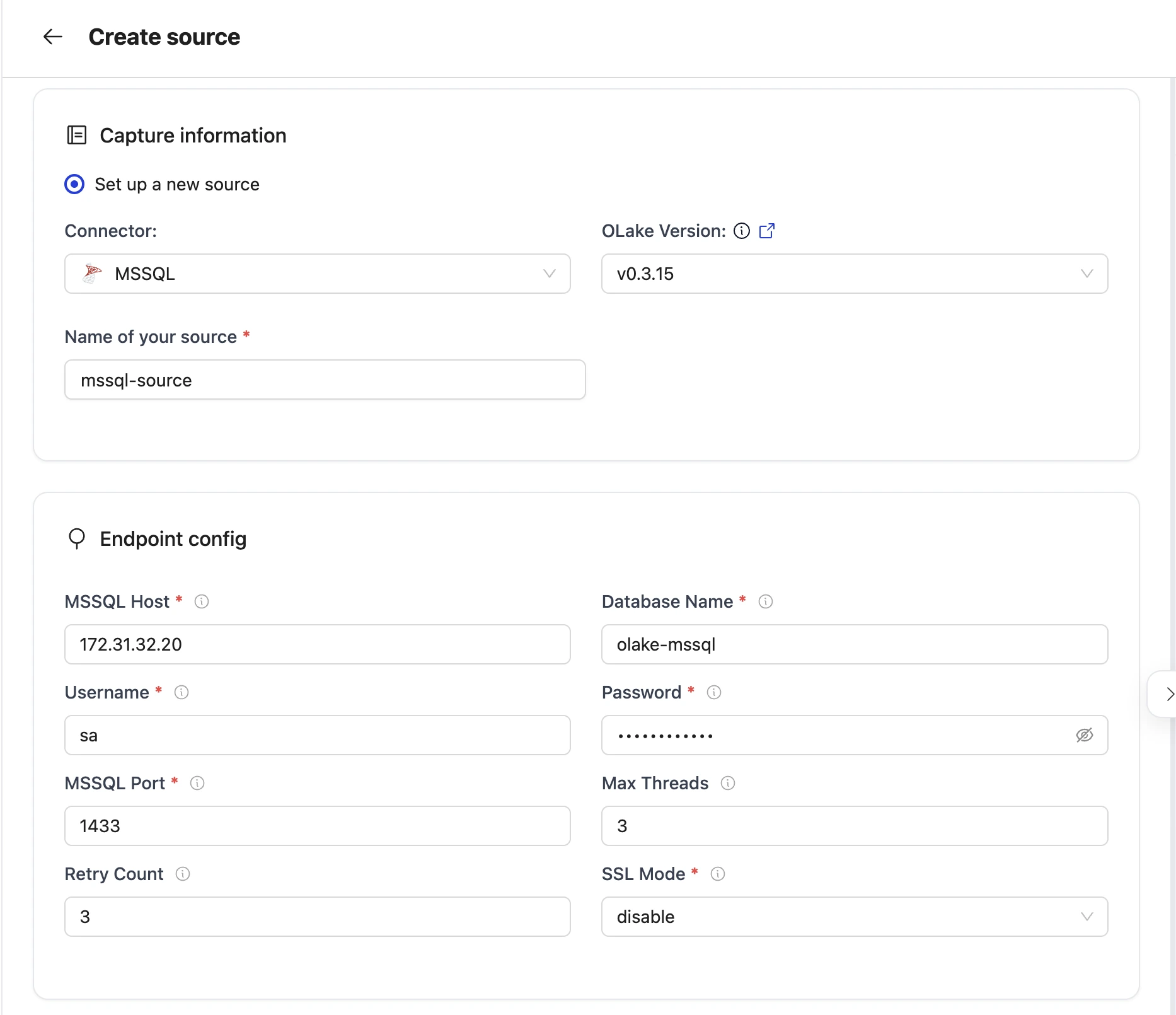
| Field | Description | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
Host required | Hostname or IP address of the MSSQL database server. | MSSQL-host |
Port required | TCP port on which the MSSQL listener is accepting connections. | 1433 |
Database Name required | The name of the target database to connect to. | olake-db |
Password required | The password corresponding to the provided username for authentication. | mssqlpwd |
Username required | Database user used to authenticate the connection. | mssql-user |
| Max Threads | Maximum number of worker threads the connector can spin up for parallel tasks. | 10 |
| SSL Mode | SSL configuration for the database connection. Contains details such as the SSL mode. | disable |
| Retry Count | Number of times the retry will take place incase of timeout before failing the sync. | 3 |
3. Test Connection
- Once the connection is validated, the MSSQL source is created. Jobs can then be configured using this source.
1. Create Configuration File
- Once the OLake CLI is setup, create a folder to store configuration files such as
source.jsonanddestination.json.
The source.json file for postgres must contain these mandatory fields.
2. Provide Configuration Details
An example source.json file will look like this:
{
"host": "mssql-server-host",
"port": 1433,
"database": "MSSQL DBName",
"username": "MSSQL Username",
"password": "MSSQL Password",
"max_threads": 3,
"retry_count": 3,
"ssl": {
"mode": "disable"
}
}
| Field | Description | Example Value | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
MSSQL Host required | Hostname or IP address of the MSSQL database server. | MSSQL-host | String |
MSSQL Port required | TCP port on which the MSSQL listener is accepting connections. | 1433 | Integer |
Database Name required | The name of the target database to connect to. | olake-db | String |
Password required | The password corresponding to the provided username for authentication. | mssqlpwd | String |
Username required | Database user used to authenticate the connection. | mssql-user | String |
| Max Threads | Maximum number of worker threads the connector can spin up for parallel tasks. | 10 | Integer |
| SSL Mode | SSL configuration for the database connection. Contains details such as the SSL mode. | disable | Object |
| Retry Count | Number of times the retry will take place incase of timeout before failing the sync. | 3 | Integer |
Similarly, destination.json file can be created inside this folder. For more information, see destination documentation.
3. Check Source Connection
To verify the database connection following command needs to be run:
docker run --pull=always \
-v "[PATH_OF_CONFIG_FOLDER]:/mnt/config" \
olakego/source-mssql:latest \
check \
--config /mnt/config/source.json
- If OLake is able to connect with MSSQL
{"connectionStatus":{"status":"SUCCEEDED"},"type":"CONNECTION_STATUS"}response is returned.
Data Type Mapping
| MSSQL Data Types | Destination Data Type |
|---|---|
| tinyint, smallint, int | int |
| bigint | bigint |
| decimal, numeric, float, smallmoney, money | double |
| real | float |
| bit | boolean |
| char, varchar, text, nchar, nvarchar, ntext, sysname, json, binary, varbinary, image, rowversion, timestamp, uniqueidentifier, geometry, geography, sql_variant, xml, hierarchyid | string |
| date, smalldatetime, datetime, datetime2, datetimeoffset | timestamp |
Date and Time Handling
During transfer, values in date, time, and timestamp columns are modified to ensure valid calendar ranges and destination compatibility.
- Case I (Year 0000):
Source dates with year0000are not valid in most destinations, so we change them to the epoch start date.
Example:0000-05-10 → 1970-01-01 - Case II (Year > 9999):
Extremely large years are capped at9999. The month and date are not affected.
Examples:10000-03-12 → 9999-03-12 - Case III (Invalid month/day):
When the month or day exceeds valid ranges (i.e. month > 12 or day > 31), or the combined date is invalid, the value is replaced with the epoch start date.
Examples:2024-13-15 → 1970-01-01,2023-04-31 → 1970-01-01
These rules apply to date, time, and timestamp columns during transfer.