Azure Database for MySQL CDC Setup Guide
Azure Database for MySQL supports CDC through binary logging on Flexible Server deployments. The service provides managed MySQL with built-in support for binary log configuration and replication capabilities.
Prerequisites:
- Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server (MySQL version 5.7+)
- Admin access to modify server parameters in Azure Portal
- The admin user or a user with administrative privileges
- Automated backups enabled with appropriate retention period
Azure Database for MySQL Single Server has limited binary logging support and is being deprecated. Migrate to Flexible Server for full CDC capabilities.
Master vs Read Replica Connection
Recommended Approach: Use Read Replica
You can connect OLake to either the master database or a read replica. We strongly recommend using a read replica for the following reasons:
- Reduced load: CDC operations don't impact your production workload
- Isolation: CDC-related configurations and monitoring are isolated from your main database
- No impact on primary: Binary log reading happens on the replica, not the primary
Read Replica Requirements for CDC:
- Read replicas in Azure Database for MySQL automatically maintain binary logs suitable for CDC
- Important: You must create the CDC user on the primary database because read replicas are read-only
- The read replica will inherit the user from the primary database
- Ensure
log_slave_updatesis enabled (usually enabled by default)
When to use Primary directly:
- For testing or development environments
- When you cannot create a read replica due to cost constraints
- For very low-traffic databases where the impact is minimal
Using a read replica means your production primary database remains unaffected by CDC operations while still providing complete binary log access for change data capture.
Steps:
1. Create Read Replica for CDC (Recommended)
If you want to use a read replica (recommended), create one first:
- In Azure Portal, navigate to your MySQL Flexible Server
- Go to Settings → Replication
- Click Add replica
- Configure the read replica:
- Choose an appropriate compute size (can be smaller than primary)
- Select the same or different region
- Configure networking (same VNet or different)
- Click Create
- Wait for the replica to be provisioned and show "Available" status
After creating the read replica, you must still create the CDC user on the primary database. The read replica will automatically inherit this user since replicas are read-only.
2. Configure Server Parameters
In the Azure Portal, navigate to your MySQL Flexible Server. Go to Settings → Server parameters and configure:
| Parameter | Value | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
log_bin | ON | Enable binary logging |
binlog_format | ROW | Capture complete row changes |
binlog_row_image | FULL | Include all columns in binary log |
gtid_mode | ON | Enable GTID mode for CDC |
expire_logs_days | 7 | Retain logs for 7 days |
server_id | Auto | Unique server identifier (managed by Azure) |
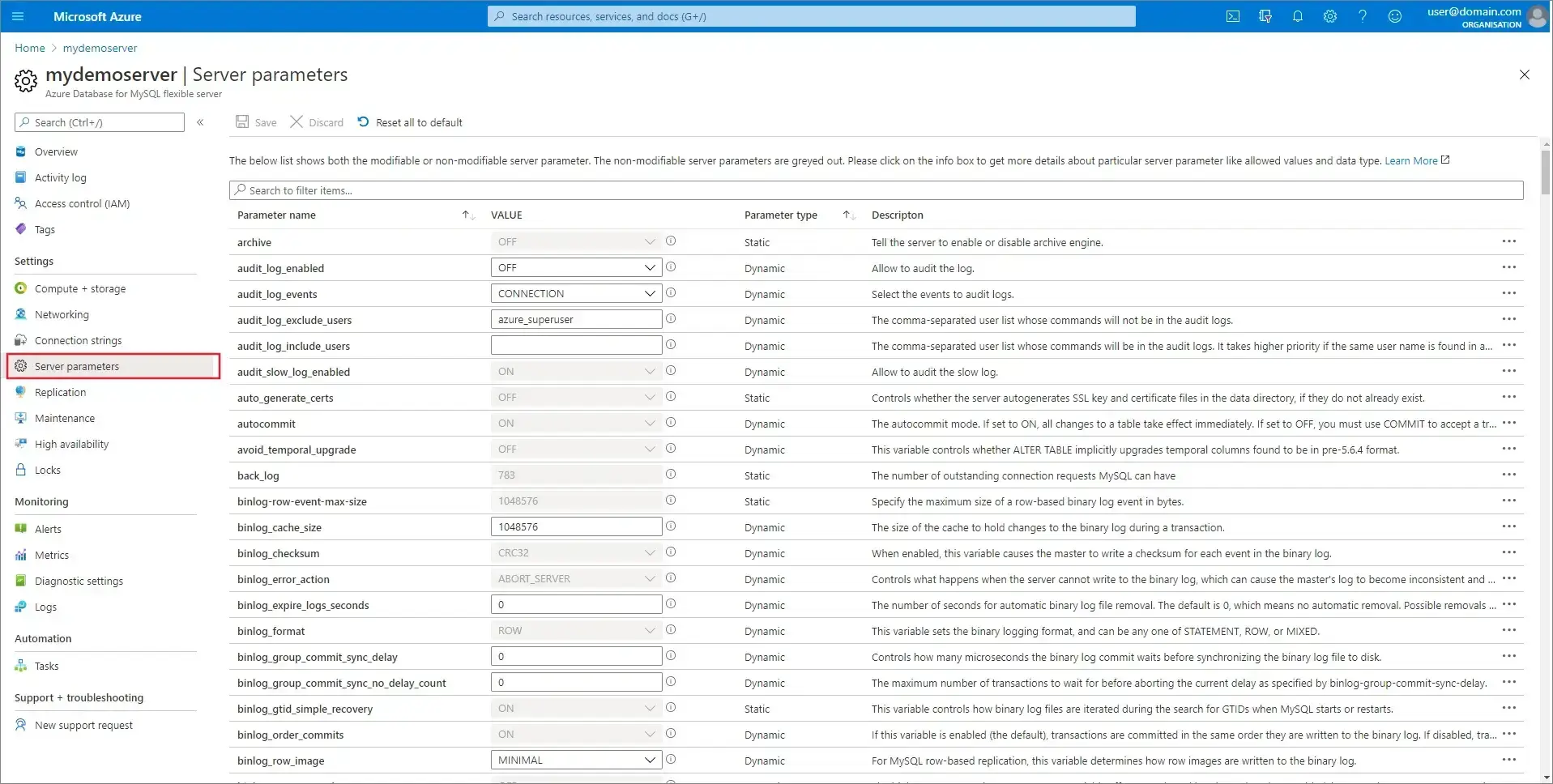
Some parameters require a server restart. Azure will indicate which parameters need a restart when you save changes.
2. Restart the Server (if required)
After saving parameter changes, restart your Flexible Server if prompted. Verify the settings after restart:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'log_bin';
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'binlog_format';
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'binlog_row_image';
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'gtid_mode';
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'expire_logs_days';
4. Create Replication User
Connect to your primary database (not the read replica) to create the CDC user. Azure admin users have administrative privileges by default. You can use the admin user or create a dedicated CDC user:
Option A: Use Admin User (Recommended for simplicity)
-- Admin user already has necessary privileges
SHOW GRANTS FOR CURRENT_USER();
Option B: Create Dedicated User
CREATE USER 'cdc_user'@'%' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'strongpassword';
GRANT SELECT, REPLICATION CLIENT, REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'cdc_user'@'%';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
The user must have REPLICATION CLIENT and REPLICATION SLAVE privileges to read binary logs. The admin user has these by default.
Optional: Restrict Database Access
For stricter security, grant access only to specific databases:
-- Grant access to specific database
CREATE USER 'cdc_user'@'%' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'strongpassword';
GRANT SELECT ON mydb.* TO 'cdc_user'@'%';
GRANT REPLICATION CLIENT, REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'cdc_user'@'%';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
5. Configure Network Access
Configure Azure's networking to allow OLake connections:
For Public Access (Flexible Server):
- In Azure Portal, go to your MySQL Flexible Server
- Navigate to Settings → Networking
- Under Firewall rules, click Add current client IP address or Add firewall rule
- Enter OLake's IP address range (Start IP and End IP)
- Click Save
For Private Access (VNet Integration):
- Ensure OLake is deployed in the same VNet or a peered VNet
- Configure appropriate Network Security Group (NSG) rules
- Allow traffic on port 3306 from OLake's subnet
6. Test Binary Logging
Verify that CDC is working correctly:
-- Check binary log status
SHOW MASTER STATUS;
-- List available binary logs
SHOW BINARY LOGS;
-- Create test data
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS test_cdc (id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, data VARCHAR(100));
INSERT INTO test_cdc (data) VALUES ('Azure MySQL CDC test');
-- Verify recent binary log events
SHOW BINLOG EVENTS LIMIT 10;
✅ Success: SHOW MASTER STATUS returns file name and position
✅ Success: SHOW BINARY LOGS lists available log files
❌ Binary logging disabled: Check server parameters and restart if needed
When configuring OLake, use a unique replica ID that doesn't conflict with existing MySQL replicas. Azure manages the server ID automatically, but OLake needs its own replica ID for connection.
7. Configure Binary Log Retention
Azure Flexible Server manages binary log retention through the expire_logs_days parameter:
-- Check current retention setting
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'expire_logs_days';
-- Retention is managed through server parameters in Azure Portal
-- Typical values: 1-99 days
For longer retention or manual management:
-- Manually purge old logs (use with caution)
PURGE BINARY LOGS BEFORE DATE_SUB(NOW(), INTERVAL 3 DAY);
Connect OLake to Your Database
When configuring OLake:
- If using a read replica: Use the read replica endpoint (e.g.,
your-replica.mysql.database.azure.com) - If using primary directly: Use the primary endpoint (e.g.,
your-primary.mysql.database.azure.com) - Port: Usually
3306 - User: The CDC user you created on the primary (format:
username@servername) - Password: The password for the CDC user
Using a read replica means your production primary database remains unaffected by CDC operations. The read replica maintains its own binary logs that are perfectly suitable for CDC operations, and it automatically inherits the CDC user from the primary.
Now that you have configured the Azure database and created the CDC user, you can add the MySQL source in OLake to build an ELT pipeline to Iceberg or Parquet. See the MySQL connector overview for a high-level walkthrough.
Troubleshooting
Configuration Issues
-
Binary Logging Not Enabled:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'log_bin'; -- Shows OFFSolution: Set
log_bin = ONin server parameters and restart the server. -
Wrong Binary Log Format:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'binlog_format'; -- Shows STATEMENT or MIXEDSolution: Set
binlog_format = ROWin server parameters and restart. -
Parameter Changes Not Applied:
- Verify the parameter was saved in Azure Portal
- Check if a restart was required and performed
- Some parameters take time to propagate
Permission Issues
-
Replication Access Denied:
ERROR: Access denied; you need (at least one of) the REPLICATION SLAVE privilege(s)Solution: Ensure the user has proper privileges:
GRANT REPLICATION CLIENT, REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'cdc_user'@'%';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES; -
Connection Denied: If OLake cannot connect:
- Check Networking settings in Azure Portal
- Verify firewall rules include OLake's IP addresses
- Ensure the connection string uses the correct server name format:
servername.mysql.database.azure.com
Network Connectivity
-
Connection Timeout: Verify:
- Azure firewall rules allow OLake's IP addresses
- Network Security Groups (NSGs) permit traffic on port 3306
- OLake is connecting to the correct server endpoint
-
SSL/TLS Issues: Azure enforces SSL by default:
- Use
sslmode=requiredin OLake connection configuration - Download Azure's SSL certificate if client certificate verification is needed
- For testing, you can disable SSL requirement in server parameters (not recommended for production)
- Use
Performance and Monitoring
-
High Binary Log Usage: Monitor through Azure Portal:
- Metrics → Log space used
- Set up alerts for high disk usage
- Consider reducing
expire_logs_daysif storage is limited
-
Connection Limits: Azure Flexible Server has connection limits based on pricing tier:
- Monitor active connections in Azure Portal
- Upgrade pricing tier if needed for more connections
-
Replication Lag: Monitor binary log position:
SHOW MASTER STATUS;
-- Compare with OLake's last processed position
Azure-Specific Issues
-
Microsoft Entra ID Authentication: If using Entra ID (Azure AD):
- Ensure the service principal is properly configured
- Use Azure AD token-based authentication in OLake configuration
- Verify the managed identity has appropriate permissions
-
High Availability Limitations:
HA Failover ImpactAzure's High Availability feature may affect binary log continuity during failovers. Monitor for any CDC disruptions after HA events and be prepared to restart OLake connections if needed.
-
Backup and Restore Impact:
- Point-in-time restores create new server instances
- Binary log positions will reset after restore operations
- Plan for full resynchronization after restore events
-
Scaling Operations:
- Compute scaling (changing pricing tier) may briefly interrupt connections
- Storage scaling is online but may affect I/O performance temporarily
- Plan CDC maintenance windows around scaling operations
Monitoring and Alerts
Set up Azure Monitor alerts for:
- Binary Log Space Usage: Alert when log space exceeds 80% of allocated storage
- Connection Count: Alert when approaching connection limits
- CPU and Memory: Monitor resource usage during CDC operations
- Failed Connections: Alert on authentication or connection failures
Example Alert Query:
AzureMetrics
| where ResourceProvider == "MICROSOFT.DBFORMYSQL"
| where MetricName == "storage_percent"
| where Average > 80
Security Best Practices
- Network Security: Use VNet integration for private connectivity
- Firewall Rules: Restrict access to specific IP ranges
- SSL/TLS: Always use encrypted connections (enabled by default)
- Authentication: Use Azure AD integration where possible
- Monitoring: Enable audit logging for security compliance
- Access Control: Use Azure RBAC for administrative access
Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server provides a robust managed platform for CDC when properly configured. The service handles most MySQL management tasks while giving you the binary logging capabilities needed for real-time data integration.