Amazon RDS MySQL CDC Setup Guide
This guide walks you through setting up Change Data Capture (CDC) for Amazon RDS MySQL instances to enable real-time data replication with OLake.
Prerequisites:
- An Amazon RDS MySQL instance (MySQL 5.7 or higher). RDS MySQL typically has binlog on if backups or replication are enabled, but format may be MIXED by default.
- A custom DB Parameter Group for MySQL (since default groups can't be edited).
- Automated backups enabled (backup retention > 0) – this is needed for long-term binlog retention on RDS
- The RDS master user or another user with the
rds_superuserandrds_replicationroles.
Master vs Read Replica Connection
Recommended Approach: Use Read Replica
You can connect OLake to either the master database or a read replica. We strongly recommend using a read replica for the following reasons:
- No downtime on production: Parameter changes and reboots only affect the read replica, not your production master
- Reduced load: CDC operations don't impact your production workload
- Isolation: CDC-related configurations are isolated from your main database
Read Replica Requirements for CDC:
- Read replicas in RDS MySQL automatically have
log_bin=ONandlog_slave_updates=ON - Read replicas maintain their own binary logs with replicated events
- You can configure CDC-specific parameters on the read replica without affecting the master
When to use Master directly:
- For testing or development environments
- When you cannot create a read replica due to cost constraints
- For very low-traffic databases where the impact is minimal
Steps:
-
Create Read Replica for CDC (Recommended): If you want to use a read replica (recommended), create one first:
- In your Amazon RDS dashboard, select your MySQL master instance
- Click Actions → Create Read Replica
- Configure the read replica:
- Choose an appropriate instance class (can be smaller than master)
- Set Public access to Publicly accessible if OLake connects from outside VPC
- Enable automated backups and set backup retention period > 0 days
- Click Create read replica
- Wait for the replica status to become "available"
tipThe read replica will automatically inherit binary logging capabilities and maintain its own binary logs suitable for CDC.
-
Enable Automated Backups (if not already): In the RDS console, check your MySQL instance's (or read replica's) backup retention setting. If "Backup retention period" is 0 (no backups), set it to at least 5 day.
Create and Configure Parameter Group
Go to Parameter Groups in AWS console, create a new DB Parameter Group for your MySQL version (e.g., "default.mysql8.0" as family if you need the name as a base). Name it e.g. "mysql8-cdc".
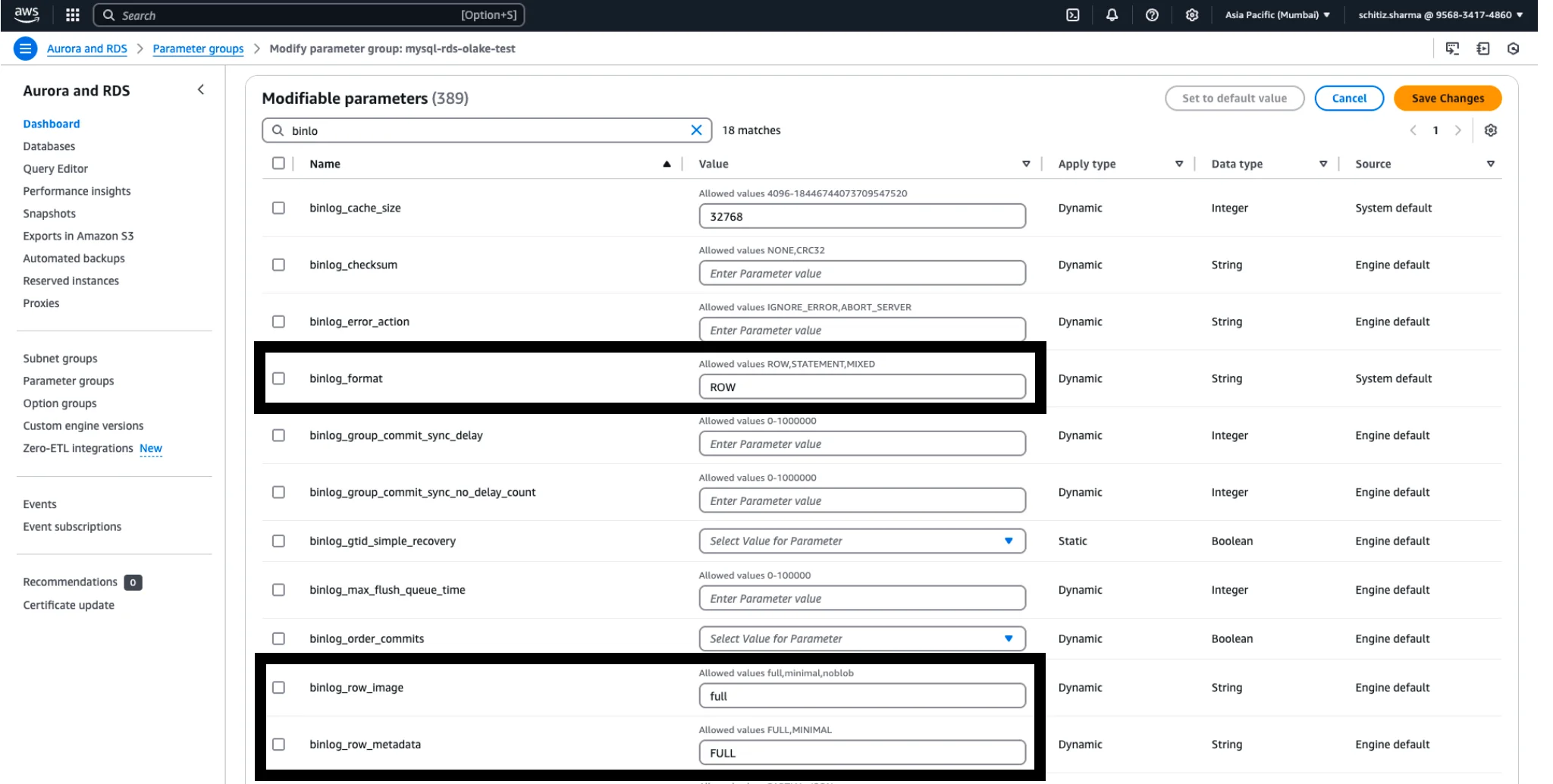
- Edit the parameters:
- Set
binlog_format = ROW - Set
binlog_row_image = FULL - Set
gtid_mode = ON - If MySQL version >= 8.0.26, you might see
binlog_expire_logs_seconds(for older MySQL 5.7, it'sexpire_logs_days). We will handle retention via a stored proc, so you can leave this default (or set to a high value as a precaution). - Ensure
log_binis ON (RDS may not show this as editable; it's managed. If it's a read-replica or multi-AZ, log_bin is automatically on).
- Set
- Save the changes. Now go to your RDS MySQL instance (or read replica if using one) and modify it to use this new DB parameter group. Apply changes and reboot the instance.
If using a read replica, apply the parameter group to the read replica, not the master. This avoids any downtime on your production master database.
Configure Security Group for OLake Access
Ensure that the RDS MySQL instance is accessible from OLake by configuring the security group:
- In the RDS instance's security group, add an inbound rule to allow connections on port 3306 (MySQL port).
- For the source, specify:
- If OLake is running on EC2: Add the security group ID of the OLake instance or the specific IP address.
- If OLake is running externally: Add the public IP address or IP range from which OLake will connect.
- For development/testing: You can temporarily use
0.0.0.0/0but this is not recommended for production.
Always use the most restrictive security group rules possible. Only allow access from the specific IP addresses or security groups where OLake is running.
-
Reboot and Verify Settings: After the instance (or read replica) reboots, verify:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'binlog_format';
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'binlog_row_image';
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'gtid_mode';They should be
ROW,FULL, andON. Also:SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'log_bin';should be "ON". If
log_binis OFF, RDS might not allow enabling it (this would be unusual, as RDS MySQL always has it on if backups or replicas are enabled). If it’s off, ensure you enabled backups and try reboot again. -
Set Binlog Retention Period: Use the RDS stored procedure on the RDS MySQL instance (or read replica) to set retention:
CALL mysql.rds_set_configuration('binlog retention hours', 24);This example sets 24 hours retention. You can set up to 168 hours (7 days) which is recommended. The ideal value depends on how long you expect the CDC connector might be down or how much lag you can tolerate. Check with:
CALL mysql.rds_show_configuration();to confirm the new setting. This setting ensures RDS doesn’t purge binlog entries for the specified hours (unless storage is under pressure). Note: By default, RDS MySQL might purge binlogs shortly after a daily automated backup; this retention overrides that behavior to keep them longer.
-
Create a Replication User: Connect to your RDS MySQL instance (or read replica) and create the CDC user:
CREATE USER 'cdc_user'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'strongpassword';
GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE, REPLICATION CLIENT ON *.* TO 'cdc_user'@'%';
GRANT SELECT ON *.* TO 'cdc_user'@'%';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Note: On RDS, users cannot be granted SUPER, so some operations (like
FLUSH LOGS) cannot be done by this user – but our privileges are enough for CDC tasks.Optional: Restrict Database Access
For stricter security, grant access only to specific databases:
-- Grant access to specific database
GRANT SELECT ON mydb.* TO 'cdc_user'@'%';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES; -
Test Binary Logging: On the RDS MySQL instance (or read replica), run:
SHOW MASTER STATUS;You should get a binlog file name and position (e.g.,
mysql-bin-changelog.000123, Position X). If you get an empty result or an error, something’s wrong with binlog config. Also try:SHOW BINARY LOGS;to list available log files. This requires
REPLICATION CLIENT(ourcdc_userhas that) or use the master user. It should list at least one binlog file.Optionally, generate a test event:
CREATE TABLE test_cdc (id INT PRIMARY KEY, val VARCHAR(10));
INSERT INTO test_cdc VALUES (1, 'rds');
SHOW BINLOG EVENTS IN '<current-binlog-file>';You might not easily guess the current binlog file name; using
MASTER STATUSto get it is easiest. But this is just a sanity check. If you see the INSERT event inSHOW BINLOG EVENTS, you know row logging is working.Replica ID ConfigurationWhen configuring OLake, use a unique replica ID that doesn't conflict with existing MySQL replicas. OLake will use a replica ID greater than 1000 by default, but you can specify your own in the source configuration.
Connect OLake to Your Database
When configuring OLake:
- If using a read replica: Use the read replica endpoint (e.g.,
your-replica.cp0rdhwjbsae.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com) - If using master directly: Use the master endpoint (e.g.,
your-master.cp0rdhwjbsae.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com) - Port: Usually
3306 - User: The
cdc_useryou created - Password: The password for the CDC user
Using a read replica means your production master database remains unaffected by CDC operations, parameter changes, and reboots. The read replica maintains its own binary logs that are perfectly suitable for CDC operations.
Now that you have configured the RDS database and created the CDC user, you can add the MySQL source in OLake to build an ELT pipeline to Iceberg or Parquet. See the MySQL connector overview for a high-level walkthrough.
Troubleshooting:
-
Parameter Application Issues: If
binlog_formatdidn’t change:- Check that the parameter group is the one attached to the instance (on RDS console, under configuration, see “Parameter group”).
- If the instance is a read replica, you need to set the parameter group on the source (actually for CDC, you’d typically use the source anyway).
- Ensure you rebooted after attaching the new param group (a common oversight is creating the group but not rebooting to apply static params).
-
Retention Issues: If RDS still purges binlogs too quickly:
- Remember that RDS will still purge logs after the set hours or if storage is under pressure. If you set 24 hours but see them gone in 6, perhaps automated backups/snapshot happened and cleared anything older than latest backup, and maybe the retention SP was not set correctly. Re-run
rds_show_configurationto confirm. - Also note: RDS for MySQL prior to 5.7 didn’t have
rds_set_configuration– but since we are focusing on modern versions, that’s fine. - If you see in
rds_show_configurationsomething likebinlog retention hours | NULL, it means it’s not set (NULL means default behavior, which is to purge after a snapshot). Run therds_set_configurationagain as the master user. Only master user can run it, not the rds_superuser role if you created one, as far as I know.
- Remember that RDS will still purge logs after the set hours or if storage is under pressure. If you set 24 hours but see them gone in 6, perhaps automated backups/snapshot happened and cleared anything older than latest backup, and maybe the retention SP was not set correctly. Re-run
-
CDC User Privileges: If your CDC connector reports errors like "The MySQL server replied with an error: ACCESS DENIED":
- Make sure the user host matches. For example, if the connector is running on an EC2 within the same VPC, connecting through the instance endpoint,
'%'works. If you set a specific host in the user (like'cdc_user'@'198.51.100.10'), and your connector’s IP changed, it would be denied. - Check
SHOW GRANTS FOR 'cdc_user'@'%'; you should see REPLICATION SLAVE, etc - If you see
ERROR 1449 (HY000): The MySQL server is running with the --read-only optionor similar, it means the user lacks privileges to perform the operation. This can happen if you try to run a snapshot or other operations that require higher privileges. - If you see
ERROR 1227 (42000): Access denied; you need (at least one of) the SUPER privilege(s) for this operation, it means the user lacks SUPER privileges. This can happen if you try to run a snapshot or other operations that require higher privileges. RDS does not allow granting SUPER, so use the master user for those operations. - If you see
ERROR 1044 (42000): Access denied for user 'cdc_user'@'%' to database 'mysql', it means the user lacks access to the mysql database. This can happen if you try to run a command that requires access to the mysql database, such asSHOW MASTER STATUS. You can either grant access to the mysql database or use the master user for those commands. - If you see
ERROR 1142 (42000): SELECT command denied to user 'cdc_user'@'%' for table 'mysql.user', it means the user lacks access to the mysql.user table. This can happen if you try to run a command that requires access to the mysql.user table, such asSHOW GRANTS FOR cdc_user. You can either grant access to the mysql.user table or use the master user for those commands. - If initial snapshot fails because of lack of privileges, consider temporarily using the master user for the snapshot then switch to the replication user for CDC.
- Make sure the user host matches. For example, if the connector is running on an EC2 within the same VPC, connecting through the instance endpoint,
-
Locked Queries / Long Locks: In RDS, global locks for backup or schema changes might interfere with CDC if they pause transactions.
-
Replication Delay / Lag: If the CDC connector falls behind and your retention is, say, 24h, and it exceeds that, it will error out with something like "Encountered change event for table X whose binlog position is no longer available" or MySQL will give an error "Could not find first log file name in binary log index file" – meaning the binlog the connector last saw has been purged. In such a case, you must re-snapshot or recover the lost events via other means. The solution is to either reduce downtime of connector or increase retention hours (up to 168). Always err on side of more retention if you can afford the storage.
-
Using Read Replica for CDC: Sometimes people consider connecting the CDC to a read replica to offload overhead. On RDS MySQL, you can connect OLake to a read replica endpoint, but you must ensure that replica has
log_binand especiallylog_slave_updatesenabled (so it writes replicated events to its own binlog). RDS read replicas by default havelog_slave_updates=ONand maintain their own binlogs (especially so you can promote them). You would have to create the replication user on the replica as well.- This is advanced; if you attempted it, ensure retention on replica as well (you can call
rds_set_configurationon the replica too).
- This is advanced; if you attempted it, ensure retention on replica as well (you can call
After completing these steps, RDS MySQL will produce a continuous stream of binlog events capturing every change, which your CDC solution will read and process. This allows near-real-time replication of MySQL data out of RDS into other systems, fulfilling the CDC use case.