Azure Database for PostgreSQL CDC Setup Guide
Azure Database for PostgreSQL supports CDC through logical replication on Flexible Server deployments. Use the native pgoutput plugin with PostgreSQL publications for CDC.
Prerequisites:
- Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server (PostgreSQL version 11+)
- Admin access to modify server parameters in Azure Portal
- The admin user or a user with
azure_pg_adminrole - Automated backups enabled with appropriate retention period
Azure Database for PostgreSQL Single Server has limited logical replication support and is being deprecated. Migrate to Flexible Server for full CDC capabilities.
Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server does not support logical replication on read replicas. Read replicas use physical replication and are read-only. OLake must connect to the primary instance for CDC functionality.
Steps:
1. Configure Server Parameters
In the Azure Portal, navigate to your PostgreSQL Flexible Server. Go to Settings → Server parameters and configure:
| Parameter | Value | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
wal_level | logical | Enable logical replication |
max_replication_slots | ≥5 | Number of concurrent CDC connections |
max_wal_senders | ≥7 | Should exceed replication slots |
wal_sender_timeout | 0 | (Optional) Prevents snapshot timeouts |
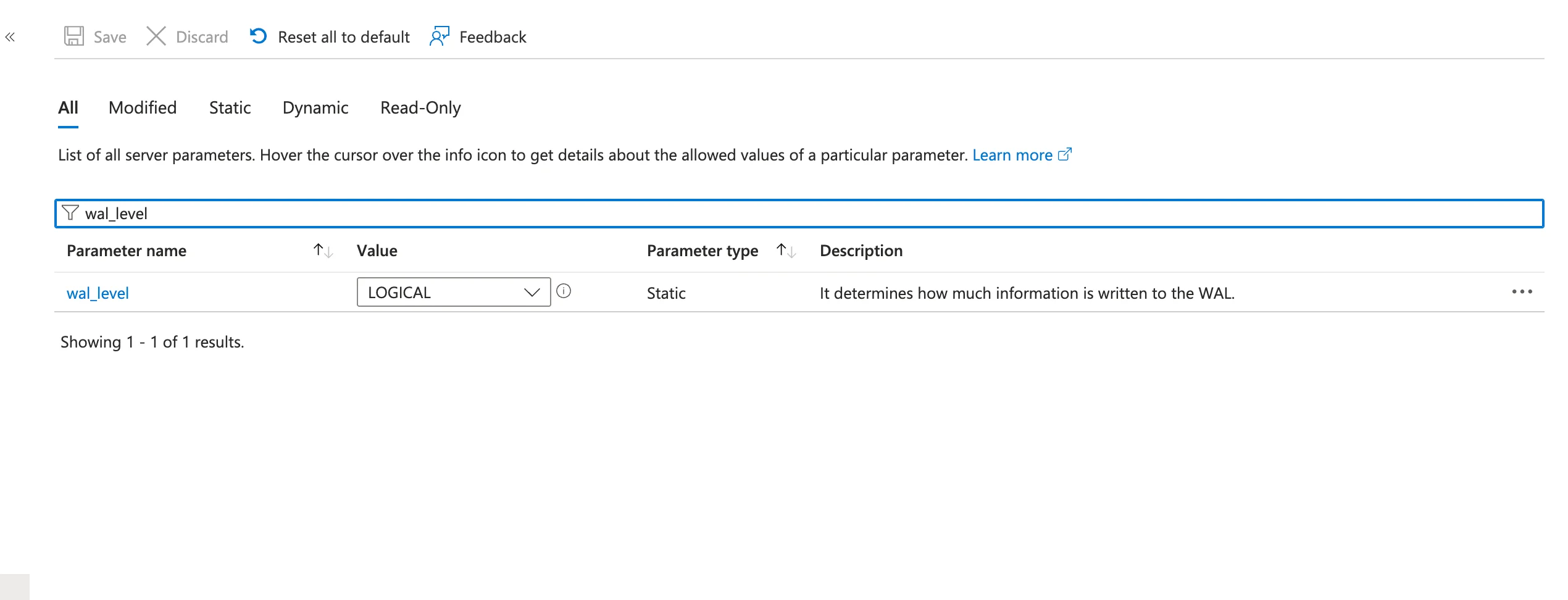
Changes to wal_level require a server restart. Azure will prompt you to restart when you save these changes.
2. Restart the Server
After saving parameter changes, restart your Flexible Server to apply the configuration. Verify the settings after restart:
SHOW wal_level;
SELECT name, setting FROM pg_settings WHERE name IN ('max_replication_slots','max_wal_senders');
3. Create Replication User
Azure admin users have the azure_pg_admin role by default. You can use the admin user or create a dedicated CDC user:
Option A: Use Admin User (Recommended for simplicity)
ALTER ROLE myadmin WITH REPLICATION;
Option B: Create Dedicated User
CREATE ROLE cdc_user WITH LOGIN PASSWORD 'strongpassword';
GRANT azure_pg_admin TO cdc_user;
ALTER ROLE cdc_user WITH REPLICATION;
The user must be a member of azure_pg_admin role to have sufficient privileges for logical replication operations in Azure.
Optional: Read-only Access for Initial Snapshot
For stricter security, grant explicit read permissions:
-- Example for the "public" schema in database mydb
GRANT CONNECT ON DATABASE mydb TO cdc_user;
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA public TO cdc_user;
GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA public TO cdc_user;
-- Ensure future tables are covered automatically
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES IN SCHEMA public GRANT SELECT ON TABLES TO cdc_user;
4. Configure Network Access
Configure Azure's networking to allow OLake connections:
For Public Access (Flexible Server):
- In Azure Portal, go to your PostgreSQL Flexible Server
- Navigate to Settings → Networking
- Under Firewall rules, click Add current client IP address or Add a firewall rule
- Enter OLake's IP address range (Start IP and End IP)
- Click Save
For Private Access (VNet Integration):
- Ensure OLake is deployed in the same VNet or a peered VNet
- Configure appropriate Network Security Group (NSG) rules
- Allow traffic on port 5432 from OLake's subnet
5. Create Publication
Publications define which tables will be replicated. Create a publication for the tables you want to monitor:
Publication Name Configuration:
Use the exact publication name that you configure in OLake UI or CLI. The publication name must match the publication parameter in your OLake source configuration.
-- Create publication for all tables in the database
CREATE PUBLICATION olake_publication FOR ALL TABLES;
-- Or create publication for specific tables
CREATE PUBLICATION olake_publication FOR TABLE public.table1, public.table2, public.table3;
-- Or create publication for all tables in a specific schema
CREATE PUBLICATION olake_publication FOR TABLES IN SCHEMA public;
Enable publish_via_partition_root for partitioned tables:
The publish_via_partition_root setting MUST be enabled to ensure data integrity when replicating partitioned tables. Without this setting, changes to partitioned tables will not be properly captured, resulting in data loss or inconsistency.
ALTER PUBLICATION olake_publication SET (publish_via_partition_root = true);
Publication Options:
-- Customize what operations are published
CREATE PUBLICATION olake_publication FOR ALL TABLES
WITH (publish = 'insert,update,delete,truncate');
-- Only publish INSERT and UPDATE operations
CREATE PUBLICATION olake_publication FOR ALL TABLES
WITH (publish = 'insert,update');
-- For partitioned tables (PostgreSQL 13+): publish changes via the partition root
CREATE PUBLICATION olake_publication FOR ALL TABLES
WITH (publish = 'insert,update,delete,truncate', publish_via_partition_root = true);
Verify Publication:
-- List all publications
SELECT * FROM pg_publication;
-- View tables in a publication
SELECT * FROM pg_publication_tables WHERE pubname = 'olake_publication';
Add Tables to Existing Publication:
-- Add a single table
ALTER PUBLICATION olake_publication ADD TABLE public.new_table;
-- Add multiple tables
ALTER PUBLICATION olake_publication ADD TABLE public.table4, public.table5;
-- Remove a table
ALTER PUBLICATION olake_publication DROP TABLE public.old_table;
6. Create Replication Slot
Set up the replication slot for OLake to consume changes:
Use the exact replication slot name that you configure in OLake UI or CLI. The slot name must match the replication_slot parameter in your OLake source configuration.
Best practices:
- Create the publication before creating the replication slot
- Create the slot in the same database that OLake will connect to (slots are per-database)
- Use a unique slot name per OLake connection; slot names cannot start with a number
-- Replace 'your_olake_slot_name' with the slot name from your OLake configuration
SELECT pg_create_logical_replication_slot('your_olake_slot_name', 'pgoutput');
Example with common slot names:
-- If your OLake source config uses "olake_slot"
SELECT pg_create_logical_replication_slot('olake_slot', 'pgoutput');
-- If your OLake source config uses "postgres_slot"
SELECT pg_create_logical_replication_slot('postgres_slot', 'pgoutput');
Verify Slot Creation:
SELECT * FROM pg_replication_slots WHERE slot_name = 'your_olake_slot_name';
7. Test Logical Decoding
Verify that CDC is working correctly with pgoutput:
-- Create test data
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS test_table (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
data TEXT,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
-- Set replica identity
ALTER TABLE test_table REPLICA IDENTITY DEFAULT;
-- Add table to publication
ALTER PUBLICATION olake_publication ADD TABLE test_table;
-- Insert test data
INSERT INTO test_table (data) VALUES ('PostgreSQL pgoutput CDC test - INSERT');
Check for changes using pg_logical_slot_peek_binary_changes:
SELECT *
FROM pg_logical_slot_peek_binary_changes(
'olake_slot', NULL, NULL,
'proto_version','1',
'publication_names','olake_publication'
);
Expected Results:
✅ Success: Returns binary change records from pgoutput
❌ Permission denied: Check user has REPLICATION role
❌ Publication not found: Verify publication exists and contains tables
❌ Slot not found: Check replication slot was created with pgoutput plugin
❌ No changes returned: Verify table has replica identity configured and is in the publication
Drop test slots after verification: SELECT pg_drop_replication_slot('test_slot');
Now that you have configured the Azure database and created the CDC user, you can add the PostgreSQL source in OLake to build an ELT pipeline to Iceberg or Parquet. See the PostgreSQL connector overview for a high-level walkthrough.
Troubleshooting
-
Permission Errors: If you see
ERROR: permission denied to create replication slot, ensure your user has bothazure_pg_adminandREPLICATIONroles. The admin user should work without additional configuration. -
Plugin Not Found: If
pgoutputis not available, verify thatwal_level = logicalis set and the server has been restarted. Ensure PostgreSQL major version is 10+. -
Connection Issues: Ensure your Azure firewall rules allow OLake's IP addresses. Also verify that the connection string includes the correct server name format:
servername.postgres.database.azure.com. -
Microsoft Entra ID Authentication: If using Entra ID (Azure AD), ensure the service principal is properly configured and has been added as a PostgreSQL user using
pgaadauth_create_principal(). -
High Availability Limitations:
HA Failover ImpactAzure's High Availability feature does not preserve logical replication slots during failovers. After a failover, you'll need to recreate the replication slot and potentially re-sync data.
-
Storage and Monitoring: Monitor Azure metrics for storage usage and transaction ID consumption. Unused logical slots can cause WAL accumulation and storage issues. Set up alerts for "Storage percent" and "Transaction log storage used" metrics.
-
Single Server Migration: If you're on the deprecated Single Server, the workaround was to create a read replica (which enabled logical replication on the primary). However, this is complex and unreliable - migrate to Flexible Server instead.
Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server provides a robust platform for CDC when properly configured. The service handles most PostgreSQL management tasks while giving you the logical replication capabilities needed for real-time data integration.