Google Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL CDC Setup Guide
Google Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL supports CDC through logical replication using the native pgoutput plugin and PostgreSQL publications. The service provides managed PostgreSQL with built-in support for logical decoding.
Prerequisites:
- Google Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL instance (PostgreSQL version 10+)
cloudsqlsuperuserprivileges (defaultpostgresuser)- Access to Google Cloud Console for configuration
- TLS enabled if connecting directly
PostgreSQL 16+: Google Cloud SQL supports logical replication on read replicas, but with limitations. Row deletions and vacuum operations on the primary may invalidate logical replication slots on read replicas, causing inconsistencies.
PostgreSQL 15 and earlier: Read replicas cannot act as publishers for logical replication. Use the primary instance for CDC functionality.
Recommendation: For production CDC workloads, connect OLake to the primary instance to avoid potential slot invalidation issues.
Steps:
1. Enable Logical Decoding
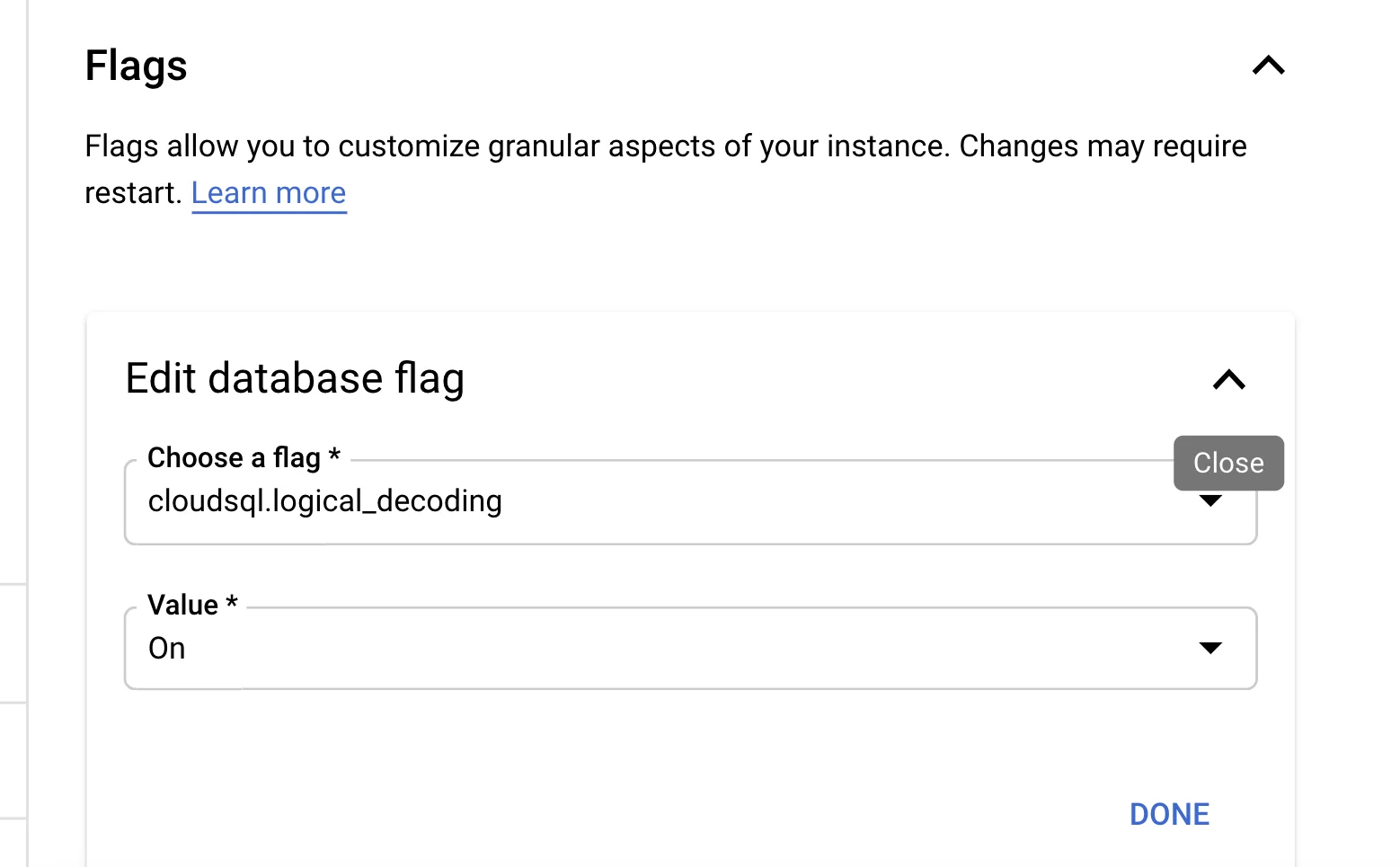
In Google Cloud Console, navigate to your Cloud SQL instance and enable the logical decoding flag:
- Go to Cloud SQL → Select your instance
- Click Edit → Flags
- Add flag:
cloudsql.logical_decoding = on - Save and Restart the instance
Verify the setting after restart:
SHOW cloudsql.logical_decoding;
2. Configure Network Access
Set up connectivity for OLake:
Option A: Direct Connection (Requires TLS)
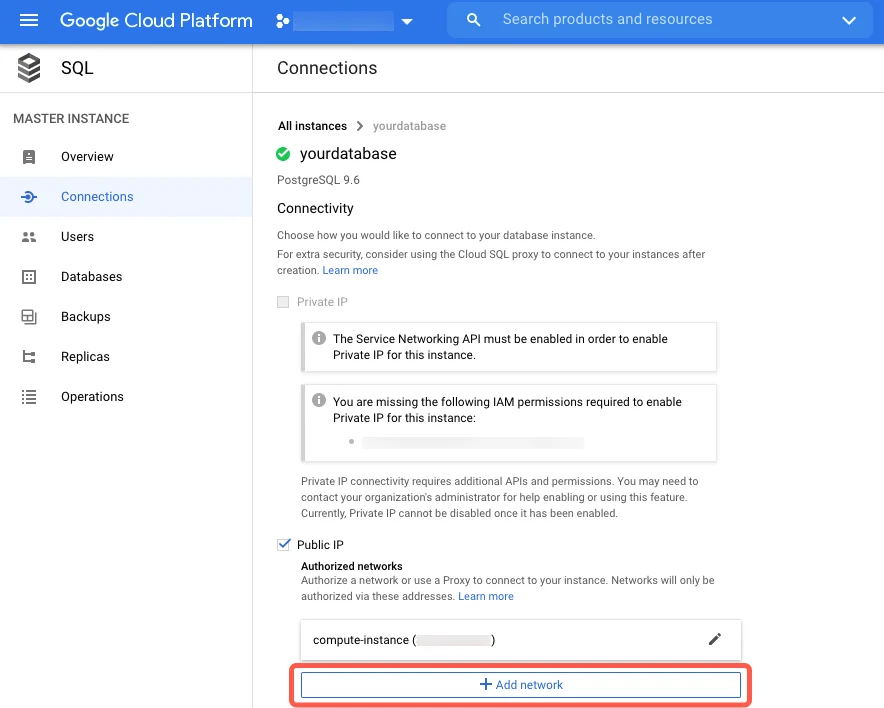
- Go to Connections → Networking
- Click Add network
- Add OLake's IP addresses with
/32CIDR - Save the configuration
Option B: Private IP Configure Private Service Connect or VPC peering for secure connectivity.
3. Create Replication User
Connect as cloudsqlsuperuser (usually postgres) and create a dedicated CDC user:
CREATE USER cdc_user WITH PASSWORD 'strongpassword';
ALTER ROLE cdc_user WITH REPLICATION;
The postgres user in Cloud SQL has cloudsqlsuperuser privileges, which includes replication permissions by default.
Optional: Read-only Access for Initial Snapshot
Grant explicit read permissions for stricter security:
-- Example for the "public" schema in database mydb
GRANT CONNECT ON DATABASE mydb TO cdc_user;
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA public TO cdc_user;
GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA public TO cdc_user;
-- Ensure future tables are covered automatically
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES IN SCHEMA public GRANT SELECT ON TABLES TO cdc_user;
4. Create Publication
Publications define which tables will be replicated. Create a publication for the tables you want to monitor:
Publication Name Configuration:
Use the exact publication name that you configure in OLake UI or CLI. The publication name must match the publication parameter in your OLake source configuration.
-- Create publication for all tables in the database
CREATE PUBLICATION olake_publication FOR ALL TABLES;
-- Or create publication for specific tables
CREATE PUBLICATION olake_publication FOR TABLE public.table1, public.table2, public.table3;
-- Or create publication for all tables in a specific schema
CREATE PUBLICATION olake_publication FOR TABLES IN SCHEMA public;
Enable publish_via_partition_root for partitioned tables:
The publish_via_partition_root setting MUST be enabled to ensure data integrity when replicating partitioned tables. Without this setting, changes to partitioned tables will not be properly captured, resulting in data loss or inconsistency.
ALTER PUBLICATION olake_publication SET (publish_via_partition_root = true);
Publication Options:
-- Customize what operations are published
CREATE PUBLICATION olake_publication FOR ALL TABLES
WITH (publish = 'insert,update,delete,truncate');
-- Only publish INSERT and UPDATE operations
CREATE PUBLICATION olake_publication FOR ALL TABLES
WITH (publish = 'insert,update');
-- For partitioned tables (PostgreSQL 13+): publish changes via the partition root
CREATE PUBLICATION olake_publication FOR ALL TABLES
WITH (publish = 'insert,update,delete,truncate', publish_via_partition_root = true);
Verify Publication:
-- List all publications
SELECT * FROM pg_publication;
-- View tables in a publication
SELECT * FROM pg_publication_tables WHERE pubname = 'olake_publication';
Add Tables to Existing Publication:
-- Add a single table
ALTER PUBLICATION olake_publication ADD TABLE public.new_table;
-- Add multiple tables
ALTER PUBLICATION olake_publication ADD TABLE public.table4, public.table5;
-- Remove a table
ALTER PUBLICATION olake_publication DROP TABLE public.old_table;
5. Create Replication Slot
Set up the replication slot for OLake to consume changes:
Use the exact replication slot name that you configure in OLake UI or CLI. The slot name must match the replication_slot parameter in your OLake source configuration.
Best practices:
- Create the publication before creating the replication slot
- Create the slot in the same database that OLake will connect to (slots are per-database)
- Use a unique slot name per OLake connection; slot names cannot start with a number
-- Replace 'your_olake_slot_name' with the slot name from your OLake configuration
SELECT pg_create_logical_replication_slot('your_olake_slot_name', 'pgoutput');
Example with common slot names:
-- If your OLake source config uses "olake_slot"
SELECT pg_create_logical_replication_slot('olake_slot', 'pgoutput');
-- If your OLake source config uses "postgres_slot"
SELECT pg_create_logical_replication_slot('postgres_slot', 'pgoutput');
Verify Slot Creation:
SELECT * FROM pg_replication_slots WHERE slot_name = 'your_olake_slot_name';
6. Test Logical Decoding
Verify that CDC is working correctly with pgoutput:
-- Create test data
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS test_table (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
data TEXT,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
-- Set replica identity
ALTER TABLE test_table REPLICA IDENTITY DEFAULT;
-- Add table to publication
ALTER PUBLICATION olake_publication ADD TABLE test_table;
-- Insert test data
INSERT INTO test_table (data) VALUES ('PostgreSQL pgoutput CDC test - INSERT');
Check for changes using pg_logical_slot_peek_binary_changes:
SELECT *
FROM pg_logical_slot_peek_binary_changes(
'olake_slot', NULL, NULL,
'proto_version','1',
'publication_names','olake_publication'
);
Expected Results:
✅ Success: Returns binary change records from pgoutput
❌ Permission denied: Check user has REPLICATION role
❌ Publication not found: Verify publication exists and contains tables
❌ Slot not found: Check replication slot was created with pgoutput plugin
❌ No changes returned: Verify table has replica identity configured and is in the publication
Now that you have configured the Google Cloud database and created the CDC user, you can add the PostgreSQL source in OLake to build an ELT pipeline to Iceberg or Parquet. See the PostgreSQL connector overview for a high-level walkthrough.
Troubleshooting
-
Flag Not Applied: If
cloudsql.logical_decodingshows asoffafter restart, verify that:- You're connected to the correct database instance
- The flag was saved before restarting
- The instance has fully restarted (check Cloud SQL logs)
-
Permission Errors: If you see
ERROR: permission denied to create replication slot:- Use the
postgresuser (which hascloudsqlsuperuserrole) - Ensure the user has
REPLICATIONprivileges:ALTER ROLE user WITH REPLICATION; - Verify the user can connect to the specific database
- Use the
-
Network Connectivity: If OLake cannot connect:
- Check that the instance has a public IP or proper private connectivity
- Verify authorized networks include OLake's IP addresses
- Ensure SSL/TLS is configured if required
- Test connectivity:
telnet your-instance-ip 5432
-
Replication Slot and Publication Issues:
- Slot names cannot start with numbers
- Each OLake connection needs a unique slot name
- Ensure a publication exists and includes your tables (
SELECT * FROM pg_publication;) - Monitor slot lag:
SELECT * FROM pg_replication_slots;
-
Read Replica Limitations:
Read Replica RequirementsLogical replication on read replicas requires PostgreSQL 16+. For earlier versions, connect OLake to the primary instance only.
-
WAL Retention: Monitor storage usage as inactive replication slots retain WAL files:
- Set up Cloud Monitoring alerts for disk usage
- Drop unused slots:
SELECT pg_drop_replication_slot('slot_name'); - Consider setting
max_slot_wal_keep_sizeto prevent runaway storage growth
-
Statement Timeout: Ensure
statement_timeoutis0or greater than 5 minutes to avoid interrupting long-running snapshot queries. -
SSL Configuration: Cloud SQL enforces SSL by default. If connecting directly:
- Use
sslmode=requirein connection strings - For client certificates, use
sslmode=verify-full - Download the server CA certificate if needed
- Use
Google Cloud SQL provides a robust managed PostgreSQL service with comprehensive CDC capabilities. The platform handles most operational concerns while providing the flexibility needed for real-time data integration.