Amazon RDS PostgreSQL CDC Setup Guide
This guide walks you through setting up Change Data Capture (CDC) for Amazon RDS PostgreSQL instances using logical replication with the native pgoutput plugin and a PostgreSQL publication for real-time data replication with OLake.
Prerequisites:
- An Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL instance (PostgreSQL 10+).
- A custom DB parameter group for this instance (the default parameter group cannot be modified).
- The RDS master user or another user with the
rds_superuserandrds_replicationroles. - Automated backups enabled (backup retention > 0) – this is needed for long-term WAL retention on RDS
Steps:
1. Create and Configure a Parameter Group
In the AWS RDS console, go to Parameter Groups and create a new parameter group for your PostgreSQL version (if you don’t already have one).
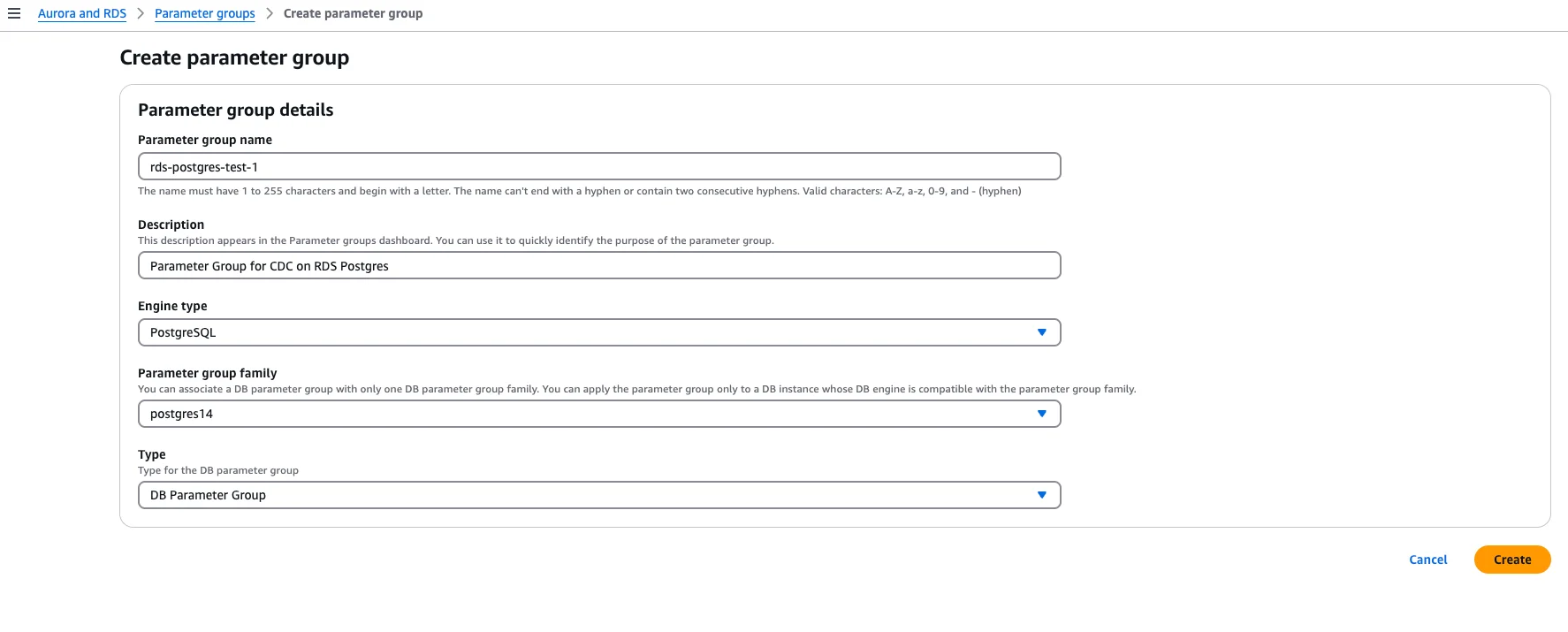
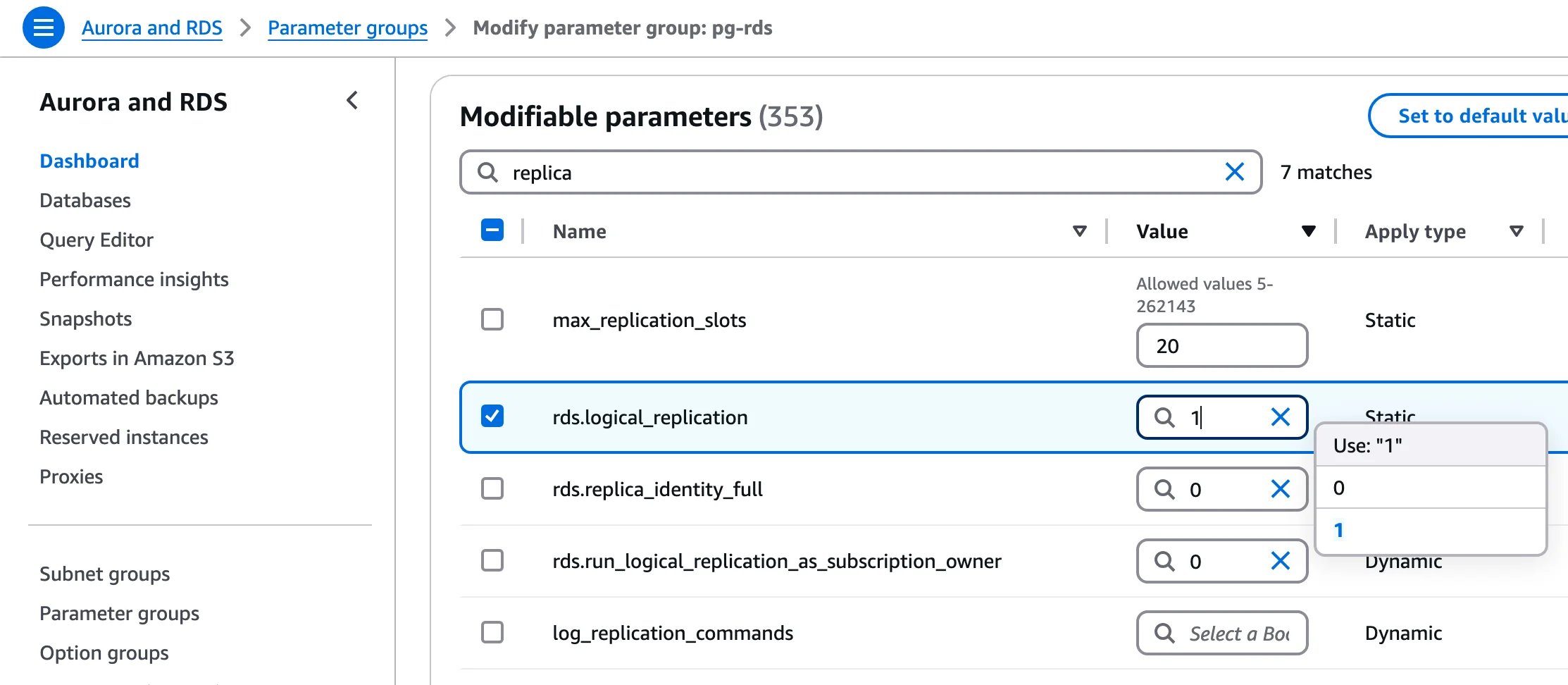
Associate the parameter group with your database instance and configure:
| Parameter | Value | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
rds.logical_replication | 1 | Enables logical replication (required for pgoutput) |
wal_level | logical | Usually set automatically by above |
max_replication_slots | ≥5 | Number of concurrent CDC connections |
max_wal_senders | ≥7 | Should exceed replication slots |
wal_sender_timeout | 0 | (Optional) Prevents snapshot timeouts |
Save the parameter group changes.
rds.logical_replication can only be turned on for read-replica instances that are running PostgreSQL 16 or later. If your replica is on an earlier major version the parameter will be ignored and logical decoding will NOT be available on that replica. Either upgrade the replica to v16+ or enable logical decoding only on the primary.
2. Reboot the RDS Instance
Reboot the database instance so that the static parameters take effect. After reboot, confirm the settings:
SELECT name, setting
FROM pg_settings
WHERE name IN ('rds.logical_replication','wal_level');
The query should show rds.logical_replication = on, and wal_level = logical.
3. Set Up a Replication User
Option A: Use Master User (Recommended for simplicity)
The RDS master user already has rds_superuser and rds_replication roles.
Option B: Create Dedicated User
CREATE USER cdc_user WITH PASSWORD 'strongpassword';
GRANT rds_replication TO cdc_user;
GRANT ALL ON SCHEMA public TO cdc_user; -- Prevents schema permission errors
Optional: Read-only Privileges for Initial Snapshot
For stricter security, grant only read access instead of ALL:
-- Example for the "public" schema in database mydb
GRANT CONNECT ON DATABASE mydb TO cdc_user;
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA public TO cdc_user;
GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA public TO cdc_user;
-- Ensure future tables are covered automatically
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES IN SCHEMA public GRANT SELECT ON TABLES TO cdc_user;
4. Create Publication
Publications define which tables will be replicated. Create a publication for the tables you want to monitor:
- Publication Name Configuration:
Use the exact publication name that you configure in OLake UI or CLI. The publication name must match the publication parameter in your OLake source configuration.
-- Create publication for all tables in the database
CREATE PUBLICATION olake_publication FOR ALL TABLES;
-- Or create publication for specific tables
CREATE PUBLICATION olake_publication FOR TABLE public.table1, public.table2, public.table3;
-- Or create publication for all tables in a specific schema
CREATE PUBLICATION olake_publication FOR TABLES IN SCHEMA public;
Enable publish_via_partition_root for partitioned tables:
The publish_via_partition_root setting MUST be enabled to ensure data integrity when replicating partitioned tables. Without this setting, changes to partitioned tables will not be properly captured, resulting in data loss or inconsistency.
ALTER PUBLICATION olake_publication SET (publish_via_partition_root = true);
Publication Options:
-- Customize what operations are published
CREATE PUBLICATION olake_publication FOR ALL TABLES
WITH (publish = 'insert,update,delete,truncate');
-- Only publish INSERT and UPDATE operations
CREATE PUBLICATION olake_publication FOR ALL TABLES
WITH (publish = 'insert,update');
-- For partitioned tables (PostgreSQL 13+): publish changes via the partition root
CREATE PUBLICATION olake_publication FOR ALL TABLES
WITH (publish = 'insert,update,delete,truncate', publish_via_partition_root = true);
Verify Publication:
-- List all publications
SELECT * FROM pg_publication;
-- View tables in a publication
SELECT * FROM pg_publication_tables WHERE pubname = 'olake_publication';
Add Tables to Existing Publication:
-- Add a single table
ALTER PUBLICATION olake_publication ADD TABLE public.new_table;
-- Add multiple tables
ALTER PUBLICATION olake_publication ADD TABLE public.table4, public.table5;
-- Remove a table
ALTER PUBLICATION olake_publication DROP TABLE public.old_table;
5. Create Replication Slot
Set up the replication slot for OLake to consume changes:
Use the exact replication slot name that you configure in OLake UI or CLI. The slot name must match the replication_slot parameter in your OLake source configuration.
Best practices:
- Create the publication before creating the replication slot
- Create the slot in the same database that OLake will connect to (slots are per-database)
- Use a unique slot name per OLake connection; slot names cannot start with a number
-- Replace 'your_olake_slot_name' with the slot name from your OLake configuration
SELECT pg_create_logical_replication_slot('your_olake_slot_name', 'pgoutput');
Example with common slot names:
-- If your OLake source config uses "olake_slot"
SELECT pg_create_logical_replication_slot('olake_slot', 'pgoutput');
-- If your OLake source config uses "postgres_slot"
SELECT pg_create_logical_replication_slot('postgres_slot', 'pgoutput');
Verify Slot Creation:
SELECT * FROM pg_replication_slots WHERE slot_name = 'your_olake_slot_name';
6. Test Logical Decoding
Verify that CDC is working correctly with pgoutput:
-- Create test data
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS test_table (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
data TEXT,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
-- Set replica identity
ALTER TABLE test_table REPLICA IDENTITY DEFAULT;
-- Add table to publication
ALTER PUBLICATION olake_publication ADD TABLE test_table;
-- Insert test data
INSERT INTO test_table (data) VALUES ('PostgreSQL pgoutput CDC test - INSERT');
Check for changes using pg_logical_slot_peek_binary_changes:
SELECT *
FROM pg_logical_slot_peek_binary_changes(
'olake_slot', NULL, NULL,
'proto_version','1',
'publication_names','olake_publication'
);
Expected Results:
✅ Success: Returns binary change records from pgoutput
❌ Permission denied: Check user has REPLICATION role
❌ Publication not found: Verify publication exists and contains tables
❌ Slot not found: Check replication slot was created with pgoutput plugin
❌ No changes returned: Verify table has replica identity configured and is in the publication
- Use the RDS endpoint, database name, and the replication user (
cdc_useror master) in your OLake configuration. Ensure your source configuration includesreplication_slotandpublicationnames. OLake will stream changes via the pgoutput logical slot. - Make sure the network setup allows the connector to reach the RDS instance (RDS must be publicly accessible or your connector is in the same VPC/network).
- Now that you have configured the database and created the CDC user, you can add the PostgreSQL source in OLake to build an ELT pipeline to Iceberg or Parquet. See the PostgreSQL connector overview for a high-level walkthrough.
Troubleshooting
-
Parameter Group Not Applying: If
rds.logical_replicationremains off after reboot, check that:- The instance is actually using your custom parameter group (in the RDS console, on the Configuration tab, verify the parameter group name).
- The parameter group family matches your engine version (e.g., “postgres12”). If not, some parameters might be ignored.
- You saved the changes and rebooted. Static parameters won’t apply without a reboot.
-
Access Issues: If the OLake reports
ERROR: permission denied for relation/sequence ...or "permission denied for schema" during snapshot or streaming, the replication user might lack SELECT privileges on those tables/schemas. Logical decoding itself does not check table ACLs for emitting changes. Grant the necessary privileges or use the master user for the initial snapshot. Also, ensure the user has therds_replicationrole to use the slot. -
Slot or Plugin Errors:
- If creating a slot yields
ERROR: permission denied to create replication slot, use the master user or a user withrds_superuserrole to create it. - If you see
ERROR: logical decoding requires wal_level "logical", it means wal_level is not logical – double-check the parameter group (maybe the DB is still running with the old param group). - If the error is about
pgoutputnot found, ensure PostgreSQL is version 10+ andrds.logical_replicationis enabled.
- If creating a slot yields
-
WAL buildup / Disk-Full: Similar to Aurora, an inactive logical slot on RDS will prevent WAL files from being purged. Monitor the WAL storage on RDS (CloudWatch metric "TransactionLogsDiskUsage"). If your CDC connector falls behind or is stopped for a while, the disk usage can grow. In extreme cases, you might get RDS events complaining that “The transaction logs have consumed XX% of storage”. To fix, either restart the CDC process to consume the backlog or drop the slot if you no longer need it. For example:
SELECT pg_drop_replication_slot('cdc_slot');Do this only if you are okay with re-snapshotting, as dropping the slot means you’ll lose the record of changes.
-
Replication Role Setup: On RDS, you cannot simply do
ALTER ROLE ... WITH REPLICATION(superuser required). Instead, AWS uses the predefined roles. The master user automatically hasrds_superuserandrds_replication. If you create a new user, you can grantrds_replicationto it. If that grant fails, it may require you to be master user (try as master). If using the master user for CDC, no action needed. In summary, many users choose the master user for CDC on RDS to avoid role issues. -
Network and Connectivity: Ensure your RDS instance is reachable:
- If it’s in a private subnet, your CDC application must have network access (consider running the CDC connector on an EC2 in the same VPC).
- If it’s publicly accessible, open the security group to the connector's IP (or corporate network) on port 5432.
- RDS may enforce SSL; use the SSL connection if required (check the parameter
rds.force_ssl).
-
Schema and Publication: Ensure new tables are added to your publication when needed. For tables without primary keys, set appropriate replica identity:
ALTER TABLE my_table REPLICA IDENTITY FULL;
By following these steps, CDC should be active on your RDS PostgreSQL instance, streaming changes through pgoutput.