Overview
The OLake S3 Source connector ingests data from Amazon S3 or S3-compatible storage (MinIO, LocalStack). It offers features like parallel chunking, checkpointing, and automatic resume for failed full loads. This connector can be used within the OLake UI or run locally via Docker for open-source workflows.
Key Features
-
Multi-Format Support: CSV files (
.csv,.csv.gz), JSON files in JSONL and Array formats (.json,.jsonl,.json.gz), and Parquet files -
Automatic Compression Handling: Transparent gzip decompression (
.gzfiles) -
Folder-Based Streams: Groups files by top-level folder into logical streams. Files are automatically grouped into streams based on folder structure. An example of bucket structure is provided below:
s3://my-bucket/data/
├── users/
│ ├── 2024-01-01/users.parquet
│ └── 2024-01-02/users.parquet
├── orders/
│ ├── 2024-01-01/orders.parquet
│ └── 2024-01-02/orders.parquet
└── products/
└── products.csv.gzIn the above example, as a result we get 3 streams created -
users,orders,products. -
S3-Compatible Services: AWS S3, MinIO, LocalStack, and other S3 APIs
Sync Modes Supported
- Full Refresh
- Incremental
How Incremental Sync Works
The S3 connector uses S3's LastModified timestamp as a cursor for incremental syncs:
How it works:
- Discovery phase adds
_last_modified_timefield to each stream - During sync, each record is injected with the file's LastModified timestamp
- State file tracks the latest
_last_modified_timeper stream - Subsequent syncs only process files with
LastModified > last_synced_timestamp
State Example:
{
"users": {
"_last_modified_time": "2024-01-15T10:30:00Z"
},
"orders": {
"_last_modified_time": "2024-01-15T11:45:00Z"
}
}
If a file's content changes and is re-uploaded to S3, it will be re-synced in incremental mode because S3 updates the LastModified timestamp.
Prerequisites
Version Prerequisites
- AWS S3 (any version) or S3-compatible service (MinIO 2020+, LocalStack 0.12+)
Connection Prerequisites
-
Read access to S3 bucket (
s3:ListBucket,s3:GetObject) -
AWS Authentication: IAM roles, environment variables, instance profiles (recommended), or static access key and secret key credentials
-
Network connectivity to S3 endpoint
-
IAM policy for S3 source access:
s3-source-iam-policy.json{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:ListBucket"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::<YOUR_S3_BUCKET>"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::<YOUR_S3_BUCKET>/*"
]
}
]
}- Replace
<YOUR_S3_BUCKET>with your actual S3 bucket name. - This policy provides read-only access required for the OLake S3 source connector.
- Replace
After initial Prerequisites are fulfilled, the configurations for S3 can be configured.
Configuration
- Use Olake UI for S3
- Use OLake CLI for S3
1. Navigate to the Source Configuration Page
- Complete the OLake UI Setup Guide
- After logging in to the OlakeUI, select the
Sourcestab from the left sidebar - Click
Create Sourceon the top right corner - Select S3 from the connector dropdown
- Provide a name for this source
2. Provide Configuration Details
- Enter S3 credentials.
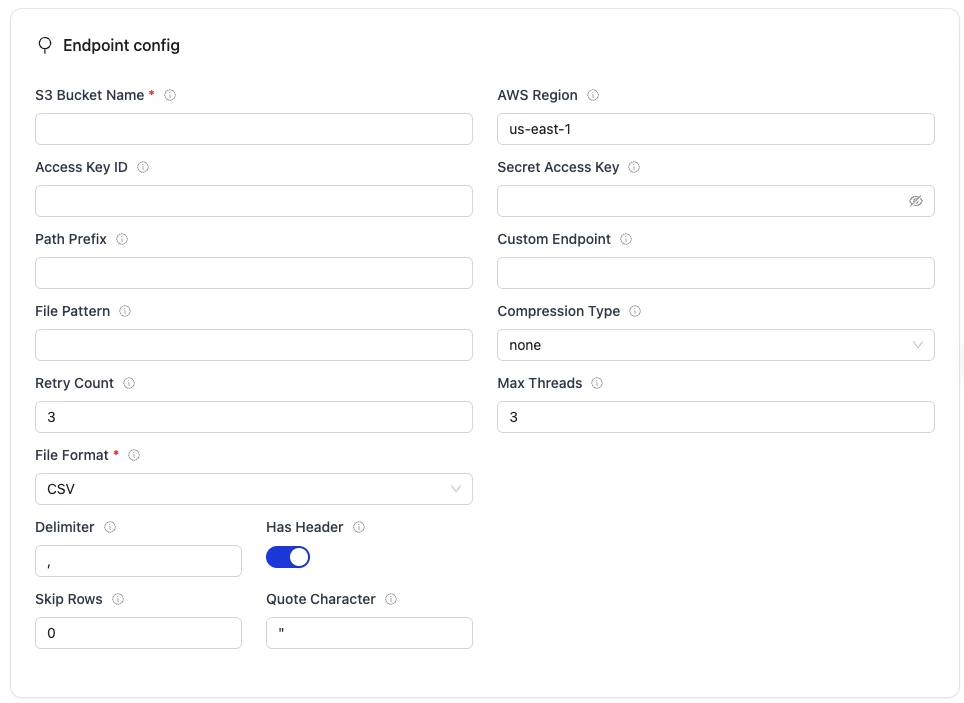
| Field | Description | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
Bucket Name required | S3 bucket name (without s3:// prefix) | my-data-warehouse |
Region required | AWS region where bucket is hosted | us-east-1 |
| Path Prefix | Optional path prefix to filter files | data/ |
| Access Key ID | AWS access key for authentication (optional - see note) | <YOUR_KEY> |
| Secret Access Key | AWS secret key for authentication (optional - see note) | <YOUR_SECRET> |
File Format required | Format of files to sync | parquet (CSV/JSON/Parquet) |
| Max Threads | Number of concurrent file processors | 10 |
| Retry Count | Number of retry attempts for failures | 3 |
- Access Key ID and Secret Access Key are optional for AWS S3. If omitted, the driver uses AWS default credential chain (IAM roles, environment variables, instance profiles, ECS task roles). This is the recommended approach for production deployments. If you provide one credential, you must provide both.
- Access Key ID, Secret Access Key and Endpoint is required for non AWS S3 services.
3. Format-Specific Configuration
- CSV Configuration
- JSON Configuration
- Parquet Configuration
Additional fields for CSV files:
| Field | Description | Default | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delimiter | Field separator character | , | ; or \t |
| Has Header | Whether first row contains column names | true | true |
| Skip Rows | Number of rows to skip at beginning | 0 | 2 |
| Quote Character | Character for quoting fields | " | ' |
Compression: Automatically detected from file extension (.csv.gz = gzipped)
Additional fields for JSON files:
| Field | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| Line Delimited | Whether JSON is JSONL format | true |
Supported Formats:
- JSONL (newline-delimited):
{"id": 1}\n{"id": 2} - JSON Array:
[{"id": 1}, {"id": 2}] - Single Object:
{"data": [...]}
Compression: Automatically detected (.json.gz, .jsonl.gz)
No additional configuration required for Parquet files.
Features:
- Schema read from Parquet metadata
- Efficient columnar reading
- Streaming support for large files
- Native type preservation
4. Test Connection
- Once the connection is validated, the S3 source is created. Jobs can then be configured using this source
- In case of connection failure, refer to the Troubleshooting section
1. Create Configuration File
- Once the Olake CLI is setup, create a folder to store configuration files such as
source.jsonanddestination.json.
The source.json file for postgres must contain these mandatory fields.
2. Provide Configuration Details
An example source.json file will look like this:
- AWS S3 (IAM Role)
- AWS S3 (Static Keys)
{
"bucket_name": "my-data-warehouse",
"region": "us-east-1",
"path_prefix": "data/",
"file_format": "parquet",
"max_threads": 10,
"retry_count": 3
}
{
"bucket_name": "my-data-warehouse",
"region": "us-east-1",
"path_prefix": "data/",
"access_key_id": "<YOUR_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID>",
"secret_access_key": "<YOUR_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY>",
"file_format": "parquet",
"max_threads": 10,
"retry_count": 3
}
| Field | Description | Example Value | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
bucket_name required | S3 bucket name (without s3:// prefix). Combined with path_prefix to form the full S3 path. Example: bucket_name="my-bucket", path_prefix="data/" results in s3://my-bucket/data/ | "my-data-warehouse" | String |
region required | AWS region where bucket is hosted | "us-east-1" | String |
path_prefix | Optional path prefix to filter files (without leading/trailing slashes) | "data" | String |
access_key_id | AWS access key ID (optional - see note below) | "<YOUR_KEY>" | String |
secret_access_key | AWS secret access key (optional - see note below) | "<YOUR_SECRET>" | String |
endpoint | Custom S3 endpoint for MinIO/LocalStack (required for non-AWS) | "http://localhost:9000" | String |
file_format required | Format of files to sync: csv, json, or parquet | "parquet" | String |
max_threads | Maximum number of concurrent file processors | 10 | Integer |
retry_count | Number of retry attempts for failed operations | 3 | Integer |
csv | CSV-specific configuration object (see CSV Format tab) | {"has_header": true, "delimiter": ","} | Object |
json | JSON-specific configuration object (see JSON Format tab) | {"line_delimited": true} | Object |
- Access Key ID and Secret Access Key are optional for AWS S3. If omitted, the driver uses AWS default credential chain (IAM roles, environment variables, instance profiles, ECS task roles). This is the recommended approach for production deployments. If you provide one credential, you must provide both.
- Access Key ID, Secret Access Key and Endpoint is required for non AWS S3 services.
3. Format-Specific Configuration Examples
- CSV Format
- JSON Format
- Parquet Format
{
"bucket_name": "source-data",
"region": "us-east-1",
"path_prefix": "csv/",
"access_key_id": "minioadmin",
"secret_access_key": "minioadmin",
"endpoint": "http://localhost:9000",
"file_format": "csv",
"max_threads": 5,
"retry_count": 3,
"csv": {
"has_header": true,
"delimiter": ",",
"skip_rows": 0,
"quote_character": "\""
}
}
CSV Configuration Fields:
| Field | Description | Default | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
delimiter | Field separator character | "," | ";" or "\\t" |
has_header | Whether first row contains column names | true | false |
skip_rows | Number of rows to skip at beginning | 0 | 2 |
quote_character | Character for quoting fields | "\"" | "'" |
Note: Gzip compression is automatically detected for .csv.gz files.
{
"bucket_name": "source-data",
"region": "us-east-1",
"path_prefix": "json/",
"access_key_id": "minioadmin",
"secret_access_key": "minioadmin",
"endpoint": "http://localhost:9000",
"file_format": "json",
"max_threads": 5,
"retry_count": 3,
"json": {
"line_delimited": true
}
}
JSON Configuration Fields:
| Field | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
line_delimited | Whether JSON is JSONL (newline-delimited) format | true |
Supported JSON Formats:
- JSONL:
{"id": 1}\n{"id": 2}\n - JSON Array:
[{"id": 1}, {"id": 2}] - Single Object:
{"data": [...]}
Format is auto-detected if line_delimited is not specified.
Note: Gzip compression is automatically detected for .json.gz and .jsonl.gz files.
{
"bucket_name": "source-data",
"region": "us-east-1",
"path_prefix": "parquet/",
"access_key_id": "minioadmin",
"secret_access_key": "minioadmin",
"endpoint": "http://localhost:9000",
"file_format": "parquet",
"max_threads": 5,
"retry_count": 3
}
Parquet Features:
- Schema automatically read from Parquet file metadata
- No additional configuration required
- Supports all Parquet data types
- Efficient streaming for large files using S3 range requests
- Native columnar reading preserves type information
4. Check Source Connection
To verify the database connection following command needs to be run:
docker run --pull=always \
-v "[PATH_OF_CONFIG_FOLDER]:/mnt/config" \
olakego/source-s3:latest \
check \
--config /mnt/config/source.json
-
If OLake is able to connect with S3
{"connectionStatus":{"status":"SUCCEEDED"},"type":"CONNECTION_STATUS"}response is returned. -
In case of connection failure, refer to the Troubleshooting section.
Data Type Mapping
| File Format | Source Data Type | Destination Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| CSV | Inferred from data | string | All CSV fields initially treated as strings |
| CSV | Numeric patterns | int, bigint, double | Integer and floating-point numbers auto-detected |
| CSV | ISO 8601 dates | timestamptz | Date/datetime strings converted to timestamp |
| CSV | Boolean values | boolean | true/false strings converted to boolean |
| JSON | string | string | JSON string fields |
| JSON | number (integer) | bigint | JSON integer values |
| JSON | number (float) | double | JSON floating-point values |
| JSON | boolean | boolean | JSON boolean values |
| JSON | object, array | string | Nested objects/arrays serialized to JSON strings |
| JSON | null | string | Null values converted to empty strings |
| Parquet | STRING, BINARY | string | Parquet string types |
| Parquet | INT32, INT64 | int, bigint | Parquet integer types |
| Parquet | FLOAT, DOUBLE | float, double | Parquet floating-point types |
| Parquet | BOOLEAN | boolean | Parquet boolean type |
| Parquet | TIMESTAMP_MILLIS | timestamptz | Parquet timestamp types |
| Parquet | DATE | date | Parquet date type |
| Parquet | DECIMAL | float | Parquet decimal types converted to float64 |
| All Formats | _last_modified_time | timestamptz | S3 LastModified metadata (added by connector) |
- CSV: Uses AND logic - examines all sampled rows to determine most restrictive type
- JSON: Auto-detects types from JSON primitives
- Parquet: Schema read directly from file metadata (no inference needed)
OLake always ingests timestamp data in UTC format, independent of the source timezone.
Date and Time Handling
During transfer, values in date, time, and timestamp columns are modified to ensure valid calendar ranges and destination compatibility.
- Case I (Year 0000):
Source dates with year0000are not valid in most destinations, so we change them to the epoch start date.
Example:0000-05-10 → 1970-01-01 - Case II (Year > 9999):
Extremely large years are capped at9999. The month and date are not affected.
Examples:10000-03-12 → 9999-03-12 - Case III (Invalid month/day):
When the month or day exceeds valid ranges (i.e. month > 12 or day > 31), or the combined date is invalid, the value is replaced with the epoch start date.
Examples:2024-13-15 → 1970-01-01,2023-04-31 → 1970-01-01
These rules apply to date, time, and timestamp columns during transfer.
Troubleshooting
1. Connection Failed - Access Denied
ERROR failed to list objects: AccessDenied: Access Denied
Cause: Insufficient IAM permissions or incorrect credentials
Solution:
- If using static credentials: Verify access key and secret key are correct
- If using IAM roles: Ensure the IAM role has proper S3 permissions attached
- Check IAM policy includes:
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["s3:ListBucket", "s3:GetObject"],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::bucket-name",
"arn:aws:s3:::bucket-name/*"
]
} - AWS Credential Chain Order:
- Static credentials in config (access_key_id, secret_access_key)
- Environment variables (AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID, AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY)
- IAM role attached to EC2 instance/ECS task
- AWS credentials file (~/.aws/credentials)
- For MinIO/LocalStack: Ensure credentials match server configuration
2. No Streams Discovered
Cause: Files not organized in folders or incorrect path_prefix
Solution:
- S3 connector requires folder structure:
bucket/prefix/stream_name/files - Check path_prefix matches your structure
- Verify file extensions match format (
.csv,.json,.parquet) - Example command to verify:
aws s3 ls s3://bucket-name/prefix/ --recursive
3. Schema Inference Failed - CSV
ERROR failed to infer schema: invalid delimiter or header configuration
Cause: Incorrect CSV configuration
Solution:
- Verify
has_headermatches file (check first row) - Check
delimiteris correct (,vs;vs\t) - Ensure all rows have same column count
- Test with a small sample file first
4. JSON Format Not Detected
Cause: Mixed JSON formats in same folder or invalid JSON
Solution:
- Keep JSONL and JSON Array formats in separate folders/streams
- Validate JSON syntax:
jq . < file.json - Ensure consistent field names across records
- Check for trailing commas or syntax errors
5. Parquet File Cannot Be Read
ERROR failed to read parquet schema: not a parquet file
Cause: Corrupted file or invalid Parquet format
Solution:
- Verify file with parquet-tools:
parquet-tools schema file.parquet - Check file wasn't corrupted during upload
- Ensure file extension is
.parquet(not.pqor other) - Re-upload file from source
6. Incremental Sync Not Working
Cause: State file not persisted or incorrect sync_mode
Solution:
- Verify
state.jsonfile location is writable - Check catalog has
sync_mode: "incremental" - Ensure
cursor_field: "_last_modified_time"is set - Confirm state file is being passed to sync command:
--state /path/to/state.json
7. MinIO Connection Timeout
ERROR dial tcp: i/o timeout
Cause: Network connectivity or incorrect endpoint
Solution:
- Check MinIO is running:
docker ps | grep minio - Test endpoint:
curl http://localhost:9000/minio/health/live - Verify endpoint format:
http://hostname:9000(include protocol) - For Docker: Use container name instead of localhost
8. Files Not Syncing Despite Being Present
Cause: File extension mismatch or compression not detected
Solution:
- Ensure file extensions match format:
- CSV:
.csvor.csv.gz - JSON:
.json,.jsonl,.json.gz,.jsonl.gz - Parquet:
.parquet
- CSV:
- Check file size is non-zero:
aws s3 ls s3://bucket/prefix/ --recursive --human-readable - Verify files are in correct folder structure
9. Out of Memory Errors
FATAL runtime: out of memory
Cause: Too many large files processed concurrently
Solution:
- Reduce
max_threadsin configuration (try 3-5) - Process fewer streams at once
- Split very large files (>5GB) before upload
- Increase container memory limits
10. Permission Denied - LocalStack
Cause: LocalStack IAM policy simulator
Solution:
- LocalStack accepts any credentials by default (
test/test) - Ensure endpoint is correct:
http://localhost:4566 - Check LocalStack is running:
docker ps | grep localstack - Verify bucket exists:
awslocal s3 ls
If the issue is not listed here, post the query on Slack to get it resolved within a few hours.
Changelog
| Date of Release | Version | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TBD | v0.4.0 | Initial S3 source connector release |