OLake Playground
OLake Playground is a self-contained environment for exploring lakehouse architecture using Apache Iceberg. It comes preconfigured with all the required components, allowing you to experience the complete workflow without manual setup.
Objective
Enable developers to experiment with an end-to-end, Iceberg-native lakehouse in minutes. Simply run a single Docker Compose docker-compose up command to launch the full stack — no service stitching, no configuration files required.
Included Components
- MySQL – Source database
- OLake – Schema discovery and CDC ingestion via an intuitive UI
- MinIO – Object store for data storage
- Temporal – Workflow orchestration for ingestion processes
- Presto – Query engine for Iceberg tables
- Trino – Query engine for Iceberg tables
- Spark – Query engine for Iceberg tables
- Trino
- Presto
- Spark
Architecture:
┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐
│ MySQL │───▶│ OLake │───▶│ MinIO │
│ (Source) │ │ (Pipeline) │ │ (Storage) │
└─────────────┘ └─────────────┘ └─────────────┘
│ │
▼ │
┌─────────────┐ │
│ Iceberg │◀───────────┘
│ REST Catalog│
└─────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────┐
│ Trino │
│ (Query UI) │
└─────────────┘Prerequisites
-
Docker: Latest version installed and running
-
Docker Compose: Latest version installed (usually included with Docker Desktop)
-
Resources: Allocate sufficient memory and CPU to Docker (e.g., 8GB+ RAM recommended)
-
Port Availability: The following ports must be available on your system:
- 8000 - OLake UI
- 8088 - Trino query engine UI
- 3000 - SQLPad UI
- 3306 - MySQL database
- 8181 - Iceberg REST catalog API
- 8443 - MinIO console UI
- 9090 - MinIO server API
Note: If any of these ports are in use, stop the conflicting services or modify the port mappings in the docker-compose-v1.yml file.
Configuration & Set Up
1. Start the demo stack
Step 1: Start base Olake stack
- New (after 30th Jan, 2026)
- Legacy (with ES)
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose-v1.yml | docker compose -f - up -d
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose.yml | docker compose -f - up -d
Step 2: Navigate and start services
cd examples/trino-tablurarest-minio-mysql
docker compose up -d
2. Accessing Services
-
Log in to the Olake UI at http://localhost:8000 with credentials
admin/password. -
Verify Source Data:
-
Access the MySQL CLI:
docker exec -it primary_mysql mysql -u root -ppassword -
Select the
weatherdatabase and query the table:USE weather;
SELECT * FROM weather LIMIT 10;This will display the first 10 rows of the
weathertable.
-
Create and Configure a Job:
Create a Job to define and run the data pipeline:
-
On the main page, click on the "Create your first Job" button. Please make sure to set the job name as
joband select a replication frequency. -
Set up the Source:
- Connector:
MySQL - Version: choose the latest available version
- Name of your source:
olake_mysql - Host:
host.docker.internal - Port:
3306 - Database:
weather - Username:
root - Password:
password - SSH Config:
No Tunnel - Update Method:
Standalone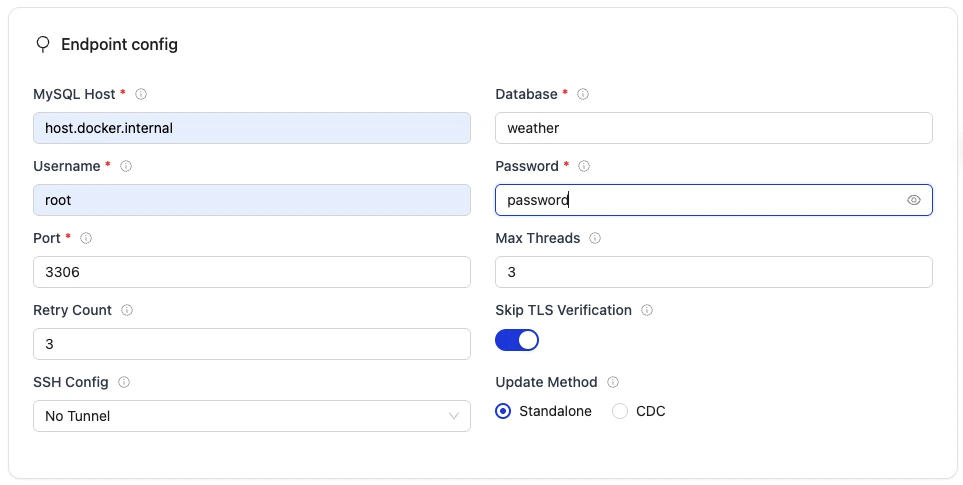
- Connector:
-
Set up the Destination:
- Connector:
Apache Iceberg - Catalog:
REST Catalog - Name of your destination:
olake_iceberg - Version: choose the latest available version
- Iceberg REST Catalog URL:
http://host.docker.internal:8181 - Iceberg S3 Path:
s3://warehouse/weather/ - S3 Endpoint (for Iceberg data files written by Olake workers):
http://host.docker.internal:9090 - AWS Region:
us-east-1 - S3 Access Key:
minio - S3 Secret Key:
minio123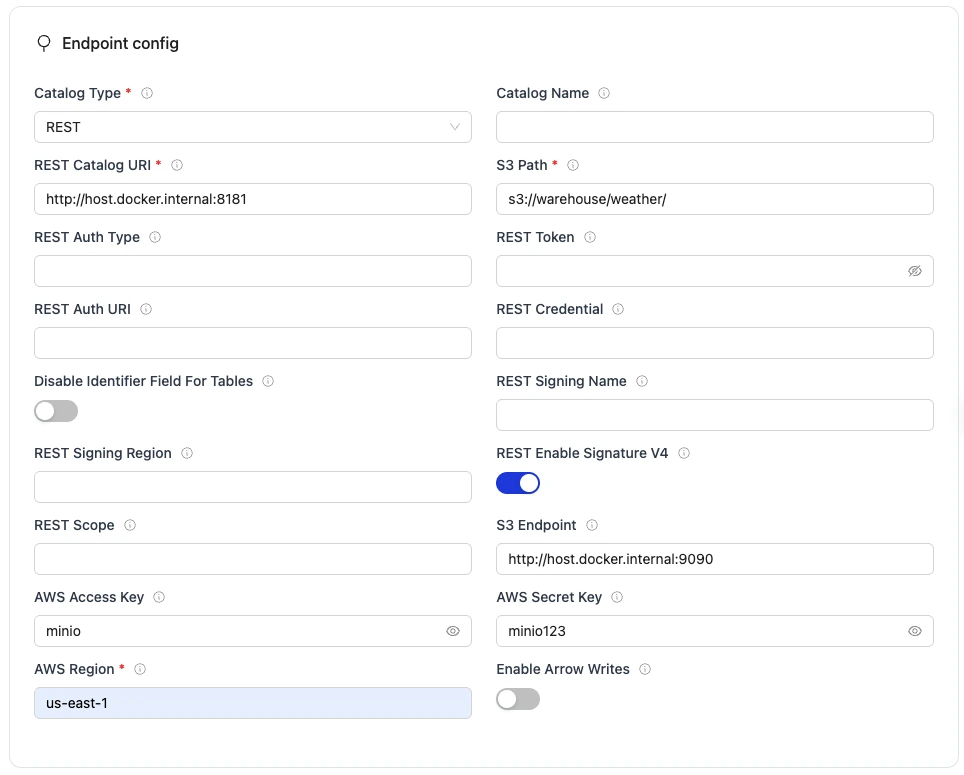
- Connector:
-
Select Streams to sync:
- Make sure that the weather table has been selected for the sync.
- Click on the weather table and make sure that the Normalisation is set to
trueusing the toggle button.
-
Save and Run the Job:
- Save the job configuration.
- Run the job manually from the UI to initiate the data pipeline from MySQL to Iceberg by clicking Sync now.
-
3. Query in Trino
- Access Trino UI:
http://localhost:3000using credentialsadmin/password - Run Queries via SQLPad UI:
- On the top left, select
OLake Demoas the database - Click on the refresh button to reload the database schemas
- Click on
job_weatherschema and theweathertable under it will be listed - Query example:
SELECT station_state, AVG(temperature_avg) as avg_temp
FROM job_weather.weather
GROUP BY station_state
ORDER BY avg_temp DESC
LIMIT 10;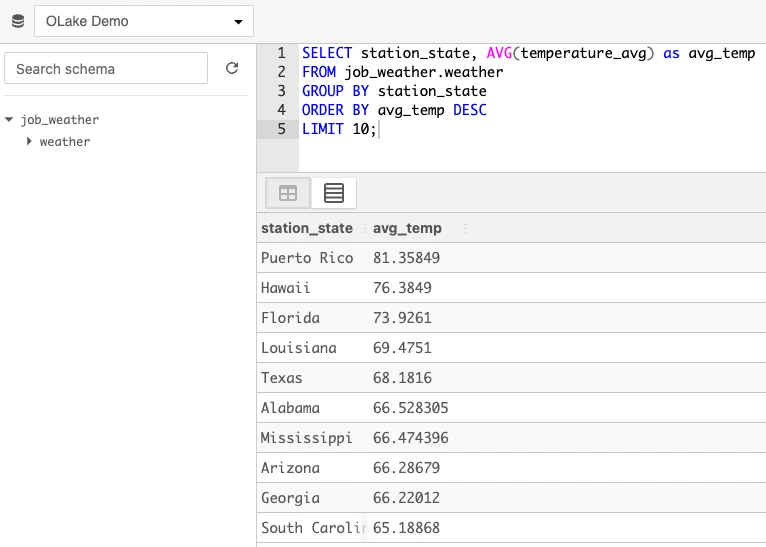
- (Optional) Run Queries via Trino CLI:
docker exec -it olake-trino-coordinator trino \
--catalog iceberg --schema job_weather \
--execute "SELECT * from weather LIMIT 10;"
Service Validation
1. View Logs
# All services
docker compose logs -f
# Specific service
docker compose logs -f trino
2. Check Service Status
# Make sure all services are running
docker compose ps
3. Verify Data Load
# Connect to MySQL
docker exec -it primary_mysql mysql -u root -ppassword weather
# Check weather table
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM weather;
SELECT * FROM weather LIMIT 5;
4. Test Trino Connection
# Check if Trino can see Iceberg tables
docker exec -it olake-trino-coordinator trino \
--catalog iceberg --schema job_weather \
--execute "SHOW TABLES;"
Troubleshooting
1. Trino can't connect to Iceberg:
- Ensure the data pipeline in OLake has run successfully
- Check that MinIO bucket contains data:
http://localhost:8443 - Verify Iceberg REST catalog is responding:
http://localhost:8181/v1/namespaces
2. MySQL connection issues:
- Wait for
init-mysql-tasksto complete data loading - Check MySQL logs:
docker compose logs primary_mysql
3. MinIO access issues:
- Check MinIO credentials in docker-compose-v1.yml match OLake destination config
- Verify bucket permissions in MinIO console
Cleanup
Step 1: Stop this example
docker compose down
Step 2: Stop base OLake stack
- New (after 30th Jan, 2026)
- Legacy (with ES)
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose-v1.yml | docker compose -f - down
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose.yml | docker compose -f - down
Architecture:
┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐
│ MySQL │───▶│ OLake │───▶│ MinIO │
│ (Source) │ │ (Pipeline) │ │ (Storage) │
└─────────────┘ └─────────────┘ └─────────────┘
│ │
▼ │
┌─────────────┐ │
│ Iceberg │◀───────────┘
│ REST Catalog│
└─────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────┐
│ Presto │
│ (Query UI) │
└─────────────┘Prerequisites
-
Docker: Latest version installed and running
-
Docker Compose: Latest version installed (usually included with Docker Desktop)
-
Resources: Allocate sufficient memory and CPU to Docker (e.g., 8GB+ RAM recommended)
-
Port Availability: The following ports must be available on your system:
- 8000 - OLake UI
- 8088 - Presto query engine UI
- 3306 - MySQL database
- 8181 - Iceberg REST catalog API
- 8443 - MinIO console UI
- 9090 - MinIO server API
Note: If any of these ports are in use, stop the conflicting services or modify the port mappings in the docker-compose-v1.yml file.
Configuration & Set Up
1. Start the demo stack
Step 1: Start base Olake stack
- New (after 30th Jan, 2026)
- Legacy (with ES)
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose-v1.yml | docker compose -f - up -d
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose.yml | docker compose -f - up -d
Step 2: Navigate and start services
cd examples/presto-tabularest-minio-mysql
docker compose up -d
2. Accessing Services
-
Log in to the Olake UI at http://localhost:8000 with credentials
admin/password. -
Verify Source Data:
-
Access the MySQL CLI:
docker exec -it primary_mysql mysql -u root -ppassword -
Select the
weatherdatabase and query the table:USE weather;
SELECT * FROM weather LIMIT 10;This will display the first 10 rows of the
weathertable.
-
Create and Configure a Job:
Create a Job to define and run the data pipeline:
- On the main page, click on the "Create your first Job" button. Set job name and replication frequency.
- Set up the Source:
- Connector:
MySQL - Version: choose the latest available version
- Name of your source:
olake_mysql - Host:
host.docker.internal - Port:
3306 - Database:
weather - Username:
root - Password:
password - SSH Config:
No Tunnel - Update Method:
Standalone
- Connector:
- Set up the Destination:
- Connector:
Apache Iceberg - Catalog:
REST Catalog - Name of your destination:
olake_iceberg - Version: choose the latest available version
- Iceberg REST Catalog URL:
http://host.docker.internal:8181 - Iceberg S3 Path:
s3://warehouse/weather/ - S3 Endpoint (for Iceberg data files written by Olake workers):
http://host.docker.internal:9090 - AWS Region:
us-east-1 - S3 Access Key:
minio - S3 Secret Key:
minio123
- Connector:
- Select Streams to sync:
- Make sure that the weather table has been selected for the sync.
- Click on the weather table and make sure that the Normalisation is set to
trueusing the toggle button.
- Save and Run the Job:
- Save the job configuration.
- Run the job manually from the UI to initiate the data pipeline from MySQL to Iceberg by clicking Sync now.
3. Query in Presto
- Access Presto UI:
http://localhost:8088
- Run Queries:
- Click on SQL CLIENT at the top
- Select Catalog:
iceberg, Schema:{job_name}_weather - Query example:
SELECT station_state, AVG(temperature_avg) as avg_temp
FROM iceberg.{job_name}_weather.weather
GROUP BY station_state
ORDER BY avg_temp DESC
LIMIT 10;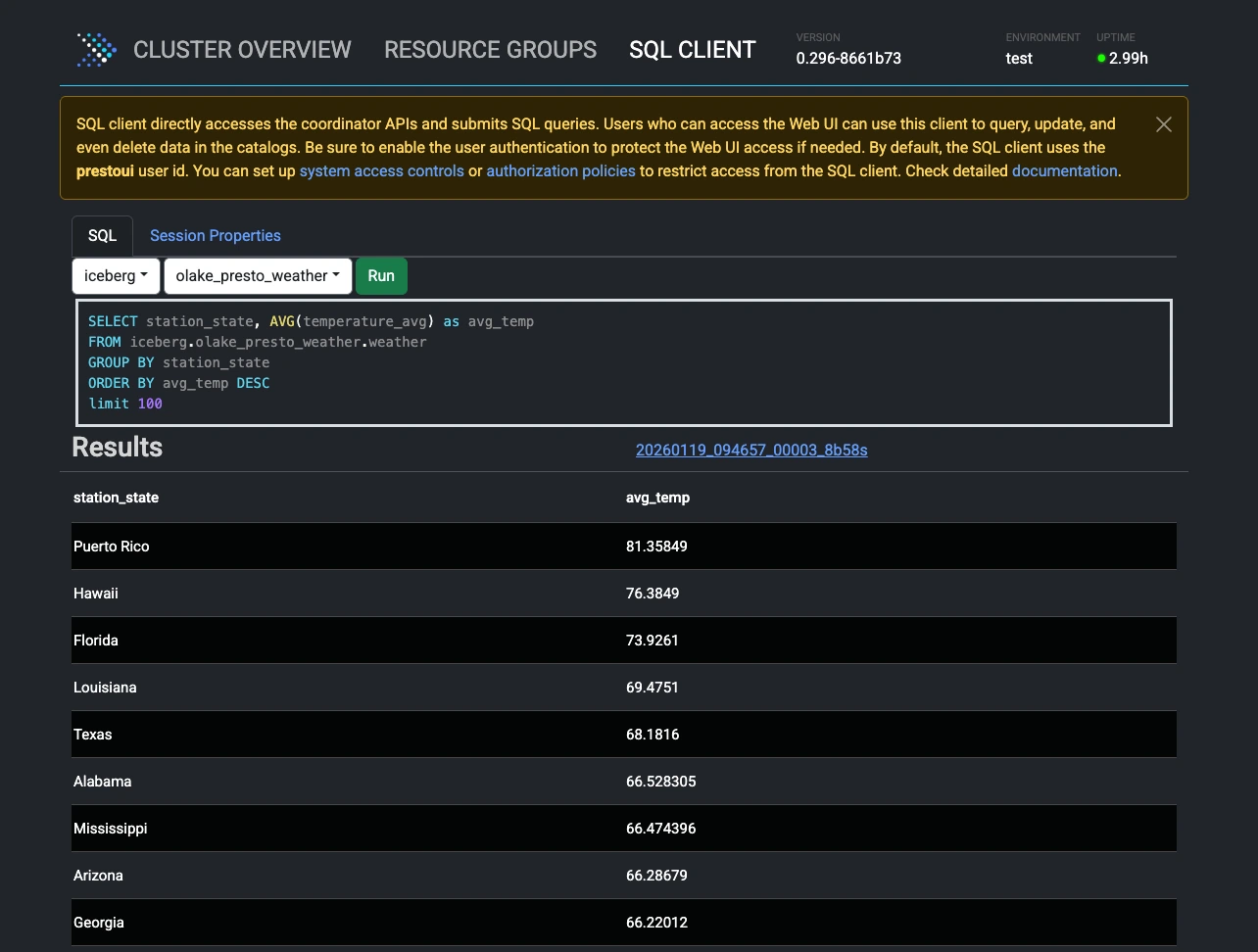
Service Validation
1. View Logs
# All services
docker compose logs -f
# Specific service
docker compose logs -f presto
2. Verify Data Load
# Connect to MySQL
docker exec -it primary_mysql mysql -u root -ppassword weather
# Check weather table
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM weather;
SELECT * FROM weather LIMIT 5;
3.Test Presto Connection
# Check if Presto can see Iceberg tables
# Make sure to replace {job_name} with your actual job name.
docker exec -it olake-presto-coordinator presto-cli --catalog iceberg --schema {job_name}_weather --execute "SHOW TABLES;"
Troubleshooting
1. Presto can't connect to Iceberg:
- Ensure the data pipeline in Olake has run successfully
- Check that MinIO bucket contains data:
http://localhost:8443 - Verify Iceberg REST catalog is responding:
http://localhost:8181/v1/namespaces
2. MySQL connection issues:
- Wait for
init-mysql-tasksto complete data loading - Check MySQL logs:
docker compose logs primary_mysql
3. MinIO access issues:
- Check MinIO credentials in docker-compose-v1.yml match OLake destination config
- Verify bucket permissions in MinIO console
Cleanup
Step 1: Stop this example
docker compose down
Step 2: Stop base Olake stack
- New (after 30th Jan, 2026)
- Legacy (with ES)
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose-v1.yml | docker compose -f - down
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose.yml | docker compose -f - down
Architecture:
┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐
│ MySQL │───▶│ OLake │───▶│ MinIO │
│ (Source) │ │ (Pipeline) │ │ (Storage) │
└─────────────┘ └─────────────┘ └─────────────┘
│ │
▼ │
┌─────────────┐ │
│ Iceberg │◀───────────┘
│ REST Catalog│
└─────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────┐
│ Spark │
│ (Query UI) │
└─────────────┘Prerequisites
-
Docker: Latest version installed and running
-
Docker Compose: Latest version installed (usually included with Docker Desktop)
-
Resources: Allocate sufficient memory and CPU to Docker (e.g., 8GB+ RAM recommended)
-
Port Availability: The following ports must be available on your system:
- 8000 - OLake UI
- 8888 - Jupyter Notebook (Spark)
- 3306 - MySQL database
- 8181 - Iceberg REST catalog API
- 9091 - MinIO console UI
- 9000 - MinIO server API
Note: If any of these ports are in use, stop the conflicting services or modify the port mappings in the docker-compose-v1.yml file.
Configuration & Set Up
1. Start the demo stack
Step 1: Start base Olake stack
- New (after 30th Jan, 2026)
- Legacy (with ES)
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose-v1.yml | docker compose -f - up -d
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose.yml | docker compose -f - up -d
Step 2: Navigate and start services
cd examples/spark-tablurarest-minio-mysql
docker compose up -d
2. Accessing Services
-
Log in to the Olake UI at http://localhost:8000 with credentials
admin/password. -
Verify Source Data:
-
Access the MySQL CLI:
docker exec -it primary_mysql mysql -u root -ppassword -
Select the
weatherdatabase and query the table:USE weather;
SELECT * FROM weather LIMIT 10;This will display the first 10 rows of the
weathertable.
-
Create and Configure a Job:
Create a Job to define and run the data pipeline:
- On the main page, click on the "Create your first Job" button. Set job name and replication frequency.
- Set up the Source:
- Connector:
MySQL - Version: choose the latest available version
- Name of your source:
olake_mysql - Host:
host.docker.internal - Port:
3306 - Database:
weather - Username:
root - Password:
password - SSH Config:
No Tunnel - Update Method:
Standalone
- Connector:
- Set up the Destination:
- Connector:
Apache Iceberg - Catalog:
REST Catalog - Name of your destination:
olake_iceberg - Version: choose the latest available version
- Iceberg REST Catalog URL:
http://host.docker.internal:8181 - Iceberg S3 Path:
s3://warehouse/weather/ - S3 Endpoint (for Iceberg data files written by Olake workers):
http://host.docker.internal:9000 - AWS Region:
us-east-1 - S3 Access Key:
minio - S3 Secret Key:
minio123
- Connector:
- Select Streams to sync:
- Make sure that the weather table has been selected for the sync.
- Click on the weather table and make sure that the Normalisation is set to
trueusing the toggle button.
- Save and Run the Job:
- Save the job configuration.
- Run the job manually from the UI to initiate the data pipeline from MySQL to Iceberg by clicking Sync now.
3. Query Data with Spark
Option 1: Using Spark SQL Shell
-
Access Spark SQL:
docker exec -it olake-spark /opt/spark/bin/spark-sql -
Run Queries:
SHOW CATALOGS;You will see the
olake_icebergcatalog available.SHOW NAMESPACES IN olake_iceberg;You will be able to see the namespace created for your table as
{job_name}_weatherNow check the tables available in the namespace:
SHOW TABLES IN {job_name}_weather;Now, query the iceberg table
SELECT * FROM olake_iceberg.{job_name}_weather.weather LIMIT 10;
Option 2: Using Jupyter Notebook
-
Access Jupyter: http://localhost:8888 (no password required)
-
Create a new python notebook and run these commands in cells:
%%sql
SHOW CATALOGS;%%sql
SHOW NAMESPACES IN olake_iceberg;%%sql
SHOW TABLES IN {job_name}_weather;%%sql
SELECT * FROM olake_iceberg.{job_name}_weather.weather LIMIT 10;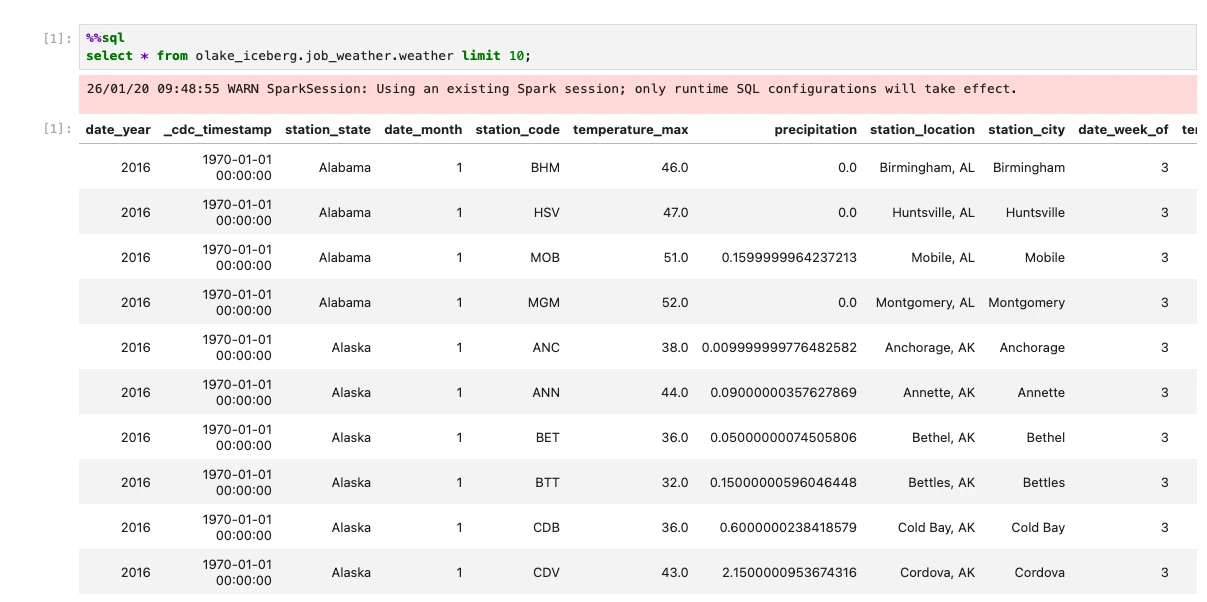
Troubleshooting
1. Spark can't connect to Iceberg:
- Ensure the data pipeline in OLake has run successfully
- Check that MinIO bucket contains data:
http://localhost:9091(credentials: minio/minio123) - Verify Iceberg REST catalog is responding:
http://localhost:8181/v1/namespaces
2. MinIO access issues:
- Check MinIO credentials in docker-compose-v1.yml match OLake destination config
- Verify bucket permissions in MinIO console
Cleanup
Step 1: Stop this example
docker compose down
Step 2: Stop base OLake stack
- New (after 30th Jan, 2026)
- Legacy (with ES)
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose-v1.yml | docker compose -f - down
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose.yml | docker compose -f - down