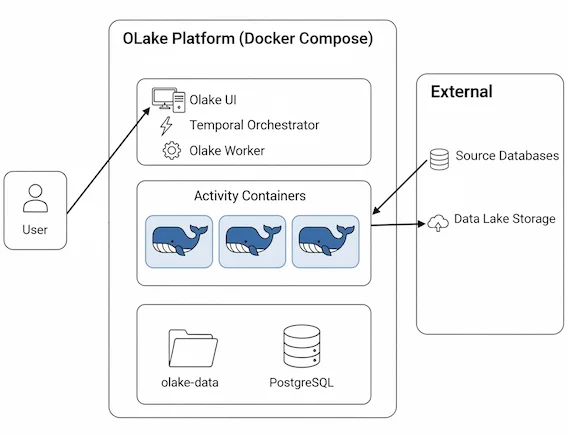
Docker Compose (OLake UI)
OLake UI provides a complete Docker Compose stack for running the replication sync using different sources with orchestration.
Components
- OLake UI: Main web interface for job management and configuration
- Temporal Worker: Background worker for processing data replication jobs
- PostgreSQL: Primary database for storing job data, configurations, sync state, and Temporal visibility data
- Temporal Server: Workflow orchestration engine for managing job execution
- Temporal UI: Web interface for monitoring workflows and debugging
- Signup Init: One-time initialization service that creates the default admin user
- Elasticsearch (Legacy only): Search and indexing backend for Temporal workflow data (deprecated in new installations)
Prerequisites
The following requirements must be met before starting:
- Docker installed (Docker Desktop recommended)
- Docker Compose (included with Docker Desktop)
- Port 8000 available on the system
- System Requirements:
- Minimum: 8 vCPU, 16 GB RAM
- Recommended: 16 vCPU, 32 GB RAM
Quick Start
One-Command Setup
The fastest way to get OLake UI running is with a single command:
- New (after 30th Jan, 2026)
- Legacy (with ES)
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose-v1.yml | docker compose -f - up -d
This setup uses Postgres for both metadata and Temporal visibility, eliminating the need for Elasticsearch.
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose.yml | docker compose -f - up -d
This setup uses Elasticsearch for Temporal visibility and Postgres for metadata. Use this if you have existing data in Elasticsearch.
This command will:
- Download the latest docker-compose.yml file
- Pull all required Docker images
- Start all services in the background
- Create a default admin user automatically
Access the Application
- OLake UI: http://localhost:8000
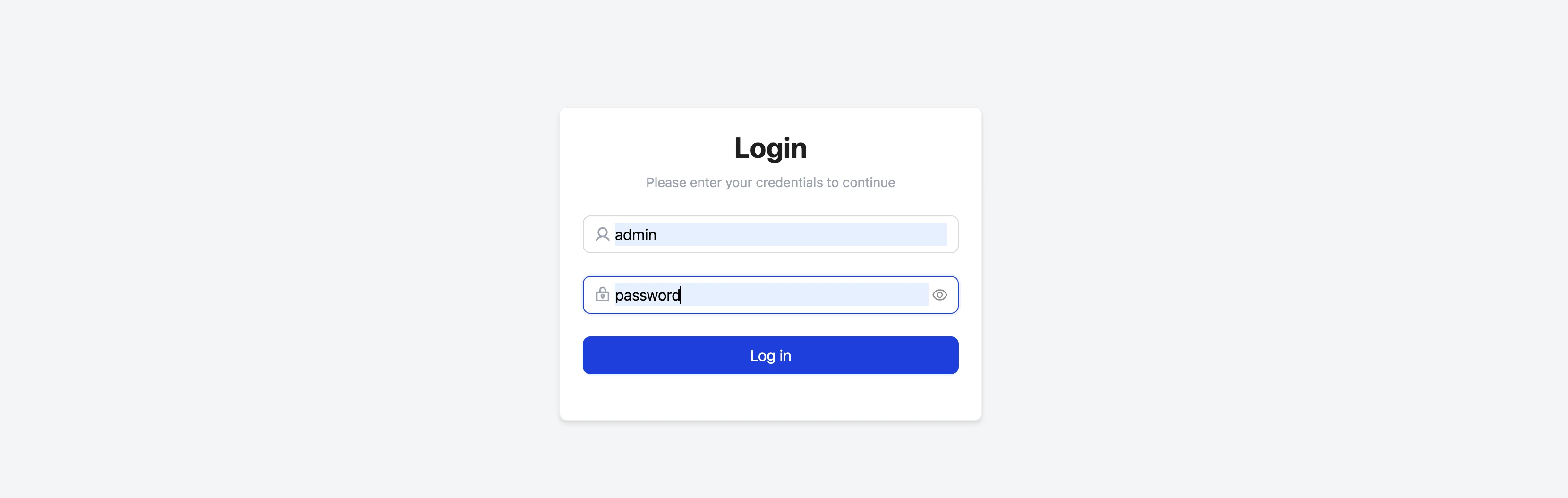
Login
The default credentials are:
- Username:
admin - Password:
password
For detailed job creation instructions, see Create Jobs or Creating First Pipeline.
Service Configuration
Changing Admin Credentials
The default admin user can be customized by editing the docker-compose.yml file before starting:
x-signup-defaults:
username: &defaultUsername "your-username"
password: &defaultPassword "your-secure-password"
email: &defaultEmail "your-email@example.com"
Updating OLake UI Version
To update OLake UI to the latest version, use the following commands based on your setup:
- New (after 30th Jan, 2026)
- Legacy (with ES)
- Upgrading Legacy to New
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose-v1.yml | docker compose -f - down && \
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose-v1.yml | docker compose -f - up -d
Note: Your data and configurations will be preserved as they are stored in persistent volumes and the olake-data directory.
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose.yml | docker compose -f - down && \
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose.yml | docker compose -f - up -d
Note: Your data and configurations will be preserved as they are stored in persistent volumes and the olake-data directory.
To move from a Legacy setup (with Elasticsearch) to the new Postgres-only visibility setup, follow these steps:
- Stop and remove the existing legacy stack:
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose.yml | docker compose -f - down
- Start the new stack:
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datazip-inc/olake-ui/master/docker-compose-v1.yml | docker compose -f - up -d
When upgrading from the Legacy setup to the New setup, existing job logs and workflow history stored in Elasticsearch will not be visible in the new setup. Only new jobs and logs generated after the upgrade will be visible.
If you require access to historical logs and job history, continue using the Legacy Setup.
Encryption Key Configuration
OLake supports encryption of source and destination configurations stored in the database. Configure the encryption key in docker-compose.yml:
-
Custom String: Provide any string (OLake generates SHA-256 hash):
x-encryption:
key: &encryptionKey "your-passphrase" -
AWS KMS: Use a AWS KMS key ARN (recommended for production):
x-encryption:
key: &encryptionKey "arn:aws:kms:us-east-1:123456789012:key/12345678-1234-1234-1234-123456789012" -
Disable Encryption: Use empty string:
x-encryption:
key: &encryptionKey "" # No Encryption
Customizing Data Directory
The default data directory can be changed by modifying the host persistence path:
x-app-defaults:
host_persistence_path: &hostPersistencePath /custom/path/to/olake-data
worker_config_volume_details: &workerConfigVolumeDetails
type: bind
source: *hostPersistencePath
target: /tmp/olake-config
This will create and use /custom/path/to/olake-data instead of the default ./olake-data directory.
External PostgreSQL Configuration
OLake supports using an external PostgreSQL instance instead of the built-in Postgres service included in the docker-compose file. This PostgreSQL stores all job data, configurations, sync state, and Temporal workflow data.
Within the compose file, an extension field named x-db-envs defines all database configuration values used by OLake and Temporal. These values can be modified to point to the external PostgreSQL instance.
x-db-envs:
DB_HOST: &DBHost postgresql
DB_PORT: &DBPort 5432
DB_USER: &DBUser temporal
DB_PASSWORD: &DBPassword temporal
DB_SSLMODE: &DBSSLMode disable
OLAKE_DB_NAME: &olakeDBName postgres
TEMPORAL_DB_NAME: &temporalDBName temporal
If connection to external PostgreSQL instance is over TLS, the following variables need to be uncommented under services.temporal.env section in the compose file:
# for TLS enabled external postgres database
SQL_TLS: true
SQL_TLS_DISABLE_HOST_VERIFICATION: true
SQL_TLS_ENABLED: true
SQL_HOST_VERIFICATION: false
A separate PostgreSQL container (postgresql service) is included by default.
When an external database is used, this service is not needed and can be stopped after all the services are started and healthy.
Service Environment Variables
Key environment variables that can be customized within x-envs section. These variables are automatically injected into the olake-ui and olake-worker containers:
x-envs:
shared: &sharedEnvs
CONTAINER_REGISTRY_BASE: ${CONTAINER_REGISTRY_BASE:-registry-1.docker.io}
OLAKE_SECRET_KEY: *encryptionKey
PERSISTENT_DIR: *hostPersistencePath
FOO: bar
KEY: value
NAME: example
Data Persistence
The Docker Compose setup creates the following data storage:
OLake Config Directory
olake-data: Local directory created in the current working directory- Contains streams configurations, connection settings, and sync state
- Persists across container restarts and recreations
- Used by OLake UI and Temporal Worker services
Docker Volumes
temporal-postgresql-data: PostgreSQL database storage- Contains workflow execution history, job metadata and sync state
- Used by the PostgreSQL service
temporal-elasticsearch-data(Legacy only): Elasticsearch search index storage- Used by the Elasticsearch service in the legacy configuration
Log Retention
OLake includes an automated log retention system that helps manage disk space by automatically cleaning up old log files. This prevents log files from accumulating indefinitely and consuming excessive storage space.
What It Does
- Runs daily at midnight (00:00 server's local timezone) using a cron job
- Deletes entire log directories that are older than the configured retention period (defaults to 30 days)
Configuration
Set the LOG_RETENTION_PERIOD environment variable in the docker-compose of olake-ui to control how long logs are kept:
# In docker-compose.yml
services:
temporal-worker:
environment:
LOG_RETENTION_PERIOD: "30" # Keep logs for 30 days
Monitoring Log Cleaner
The log cleanup process can be monitored through the logs of the temporal-worker service defined in the docker-compose configuration for olake-ui.
When the log cleaner starts, it emits a log entry indicating the beginning of the process:
Log cleaner started...
Every time the cron job runs, it emits the following log:
Running log cleaner...
As each log directory is deleted, a log entry is generated showing the full path of the directory being removed:
Deleting folder /path/to/olake/logs
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Port Conflicts
If port binding errors occur:
- Check what's using the ports:
lsof -i :8000(on macOS/Linux) - Stop conflicting services or change ports in
docker-compose.yml
Database Connection Issues
- Ensure PostgreSQL container is healthy:
docker compose ps - Check PostgreSQL logs:
docker compose logs postgresql
Memory Issues
- Ensure Docker has at least 4GB RAM allocated
- Check Docker resource usage:
docker stats
Permission Issues
- On Linux, ensure the user is in the docker group
- Check file permissions for the
./olake-data/directory (or custom path if modified)
Reset Everything
The stack can be completely reset with:
docker compose down -v # Removes containers and volumes
docker compose up -d # Fresh start
Warning: This will delete all job data and configurations.