OLake UI for Offline Environments (AWS)
OLake UI can be deployed in offline or air‑gapped AWS environments by using an Amazon ECR pull‑through cache to mirror required Docker images. This guide outlines how to configure the pull-through cache, pre‑pull connector images, and run OLake UI.
ECR pull-through cache is an AWS service that automatically mirrors and caches Docker images from external registries like Docker Hub into your private ECR registry for offline access.
Prerequisites
The following are required to begin:
- An active AWS account with
Administrator AccessIAM permissions - A Docker Hub account with permission to generate
Personal Access Token - Docker installed and configured on the machine where OLake UI is set up
- The AWS CLI installed and configured on the machine where OLake UI is set up
1. Docker Hub Access Token
To authenticate ECR Pull Through Cache with Docker Hub, a Personal Access Token (PAT) must be created. This token will be used by AWS to pull images.
- Log in to the Docker Hub account
- Navigate to Account Settings > Personal access tokens
- Provide a description for the token (e.g., "Access Token for ECR pull-through cache")
- Set expiration date to None
- Set the access permissions. For this use case, Public Repo Read-only access is sufficient
- Click Generate
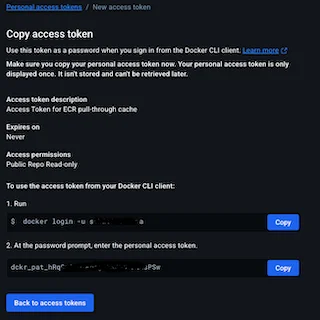
Copy the generated token and store it in a secure location. The token will not be visible again after the window is closed.
For more detailed instructions, refer to the official Docker documentation on creating access tokens.
2. Store Docker Hub Credentials in AWS Secrets Manager
Next, the Docker Hub credentials must be securely stored in AWS Secrets Manager. This allows ECR to authenticate with Docker Hub without exposing credentials in code or configuration files.
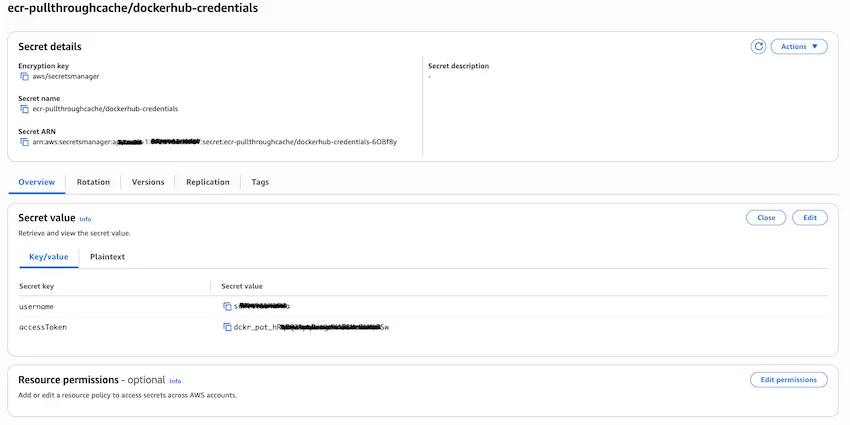
- Open the AWS Management Console and navigate to Secrets Manager
- Click Store a new secret
- For the Secret type, select Other type of secret
- In the Key/value pairs section, create two key-value pairs:
- Key:
username, Value: Your Docker Hub username - Key:
accessToken, Value: The Docker Hub Personal Access Token created in the previous step
- Key:
- For the Secret name, enter a descriptive name with the prefix
ecr-pullthroughcache/. For example:ecr-pullthroughcache/dockerhub-credentials - Skip to the Review step and leave other values as default
- Click Store to save the secret
3. Create the ECR Pull-Through Cache Rule
Now, the pull-through cache rule can be created in ECR. This rule instructs ECR to cache images from Docker Hub whenever they are pulled through the private registry.
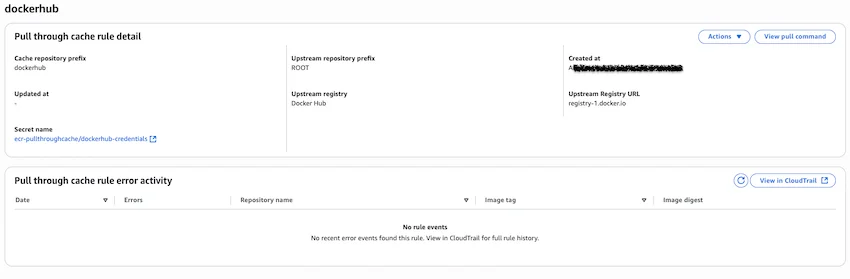
- In the AWS Management Console, navigate to Elastic Container Registry (ECR)
- In the left-hand menu, under Private registry click on Features and Settings to expand, select Pull through cache
- Click Add rule
- For the Upstream registry, select Docker Hub (note that
registry-1.docker.iois the official Docker Hub registry by default) - For Authentication, select Use an existing AWS secret and choose the secret created in Step 2
- For the Cache repository prefix, enter a prefix that will be used to create new repositories for the cached images (e.g.,
dockerhub) - For the Upstream namespace, choose No Prefix
- Click Create
4. Configure IAM Permissions
With the ECR Pull-through cache rule created, the necessary IAM permissions can be configured. An IAM role with the correct policy must be attached to the machine where OLake UI will be run.
The policy should include the following permissions. Ensure the resource ARN is updated with the correct region, account ID, and the ECR repository prefix created in the previous section:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "ECRLogin",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "ecr:GetAuthorizationToken",
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Sid": "PullFromDockerHubWithPrefix",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ecr:CreatePullThroughCacheRule",
"ecr:CreateRepository",
"ecr:GetDownloadUrlForLayer",
"ecr:GetAuthorizationToken",
"ecr:BatchImportUpstreamImage",
"ecr:BatchGetImage",
"ecr:GetImageCopyStatus",
"ecr:InitiateLayerUpload",
"ecr:UploadLayerPart",
"ecr:CompleteLayerUpload",
"ecr:PutImage",
"ecr:ListImages",
"ecr:DescribeImages"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:ecr:<region>:<aws_account_id>:repository/<ecr_repository_prefix>",
"arn:aws:ecr:<region>:<aws_account_id>:repository/<ecr_repository_prefix>/*"
]
}
]
}
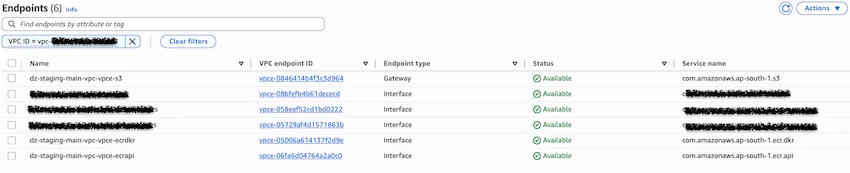
5. Configure VPC Endpoints for Offline Environments
For a truly isolated environment, VPC endpoints need to be configured. This allows instances to communicate with AWS services without traversing the public internet.
The following VPC endpoints need to be created:
com.amazonaws.<region>.ecr.apicom.amazonaws.<region>.ecr.dkrcom.amazonaws.<region>.s3(ECR uses S3 to store image layers)
For detailed instructions on creating VPC endpoints, please refer to the AWS documentation.
6. Pre-pull Connector Images
The OLake UI spins up separate Docker containers for different data sources (connectors). These connector images must also be pulled through the ECR pull-through cache before starting the main application stack.
Run the following commands on the machine where Docker Compose will be run. These commands will pull the necessary connector images and ensure they are cached in the private ECR. Replace <version> with the specific connector version required. Only use stable release versions (e.g., v0.1.8).
# Docker login for AWS ECR repository
aws ecr get-login-password --region <region> | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin <account_id>.dkr.ecr.<region>.amazonaws.com
# MySQL Connector
docker pull <aws_account_id>.dkr.ecr.<region>.amazonaws.com/<ecr_repository_prefix>/olakego/source-mysql:<version>
# PostgreSQL Connector
docker pull <aws_account_id>.dkr.ecr.<region>.amazonaws.com/<ecr_repository_prefix>/olakego/source-postgres:<version>
# MongoDB Connector
docker pull <aws_account_id>.dkr.ecr.<region>.amazonaws.com/<ecr_repository_prefix>/olakego/source-mongodb:<version>
# Oracle DB Connector
docker pull <aws_account_id>.dkr.ecr.<region>.amazonaws.com/<ecr_repository_prefix>/olakego/source-oracle:<version>
This pre-pull step is a one-time action for each connector version. Once an image is pulled, it is cached within the private ECR.
7. Run the Application Stack
With the pull-through cache configured and connector images pre-pulled, the main OLake application can be started. The OLake docker-compose.yml is designed to use an environment variable to specify the container registry. This makes it easy to switch from Docker Hub to a private ECR.
Configure the Environment
In the same directory where the OLake docker-compose.yml file is located, a new file named .env must be created.
The .env file should contain the following line:
CONTAINER_REGISTRY_BASE="<aws_account_id>.dkr.ecr.<region>.amazonaws.com/<ecr_repository_prefix>"
# Example: CONTAINER_REGISTRY_BASE="111222333444.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/dockerhub"
Replace <aws_account_id> and <region> with the appropriate AWS account ID and region. The <ecr_repository_prefix> must be replaced with the value created earlier.
The docker-compose.yml file for OLake is already configured to use this CONTAINER_REGISTRY_BASE variable for all service images. No modifications to the docker-compose.yml file itself are necessary.
Start OLake UI
With the environment configured, start the OLake UI stack:
# Start the application stack
docker-compose up -d
Access the OLake UI
The OLake UI will be available at:
- URL: http://localhost:8000
- Username:
admin - Password:
password
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
ECR Authentication Failures:
- Ensure the IAM role has the correct ECR permissions
Image Pull Failures:
- Confirm the pull-through cache rule is correctly configured
- Verify the Docker Hub credentials in Secrets Manager
- Ensure VPC endpoints are properly set up for offline environments
Service Startup Issues:
- Check that all required images have been pre-pulled
- Verify the
.envfile contains the correct registry configuration - Review Docker Compose logs:
docker-compose logs